成为ob贡献者(09):如何证明采用了PALF设计就是安全的
文章目录
来监督,哪天没打卡 私信我
第5章节:数据变更同步
 原文:
原文:
Besides serving transactions, distributed databases also act as the
source of data flow. Downstream applications can be deployed to
provide various services by synchronizing data changes recorded
in physical logs.
This section introduces two typical physical log
synchronization scenarios in OceanBase, describes what challenges
they bring to PALF, and depicts how to address these challenges by
utilizing features of PALF.
翻译:
除了处理事务,分布式数据库还充当数据流的源头。下游应用可以通过同步物理日志中记录的数据更改来部署,从而提供各种服务。
本节介绍了OceanBase中两种典型的物理日志同步场景,描述了它们给PALF带来的挑战,并阐述了如何利用PALF的特性来解决这些挑战。
通俗理解:
分布式数据库不仅仅是处理事务(如存取数据)的地方,它们还扮演着数据流的起点。下游系统(指其他依赖这些数据的应用或服务)可以通过获取数据库中记录的数据变化(比如用户修改了什么信息),来实现各种功能,比如数据分析、实时报告等。
在OceanBase数据库中,有两种常见的方式来同步这些数据变化。本节主要讲解这两种方式,以及它们给数据库的高可用性(PALF)带来了哪些问题,最后介绍如何利用PALF的特性来解决这些问题。
简单来说,数据库不仅存储和处理数据,还能把数据的变动告诉其他系统,这样其他系统就能根据最新的数据做相应的处理。而OceanBase在这方面有两种常用的方法,但这些方法也带来了一些挑战,文中会讲解应该如何应对这些挑战。
5.1
原文:
When clients write data to databases, records of modifications are
appended to the leader of the PALF group and replicated to followers.
Besides replicating logs within the database, data changes can
be synchronized out of the database for richer functions.
There are two typical scenarios in the OceanBase database: physical standby databases and database restore
翻译:
当客户端向数据库写入数据时,修改记录会被追加到PALF组的主节点,并复制到从节点。在数据库内部复制日志的同时,数据变化也可以被同步到数据库外部,以实现更丰富的功能。在OceanBase数据库中,主要有两种典型场景:物理备用数据库和数据库恢复
通俗理解:
想象一下,你在银行存钱,每次存钱都会记录一条转账记录。银行的系统会把这条记录同时保存到主要的记录本(主节点)和几个副本记录本(从节点),这样即使主要记录本坏了,副本记录本还能保证数据不丢失。
除了在银行内部保存这些记录,银行还可以把这些记录送到其他地方,比如给审计部门或者数据分析部门,用于更广泛的用途。在OceanBase数据库中,这种技术有两种主要用途:
-
物理备用数据库:就像银行有多个分行各自保存一份记录副本,数据库也可以有多个物理备用数据库,确保在主数据库出问题时,备用数据库能立即接管,保证服务不中断。
-
数据库恢复:如果数据库因为意外情况(比如系统故障)导致数据丢失,可以通过之前保存的记录快速恢复数据,确保数据安全。
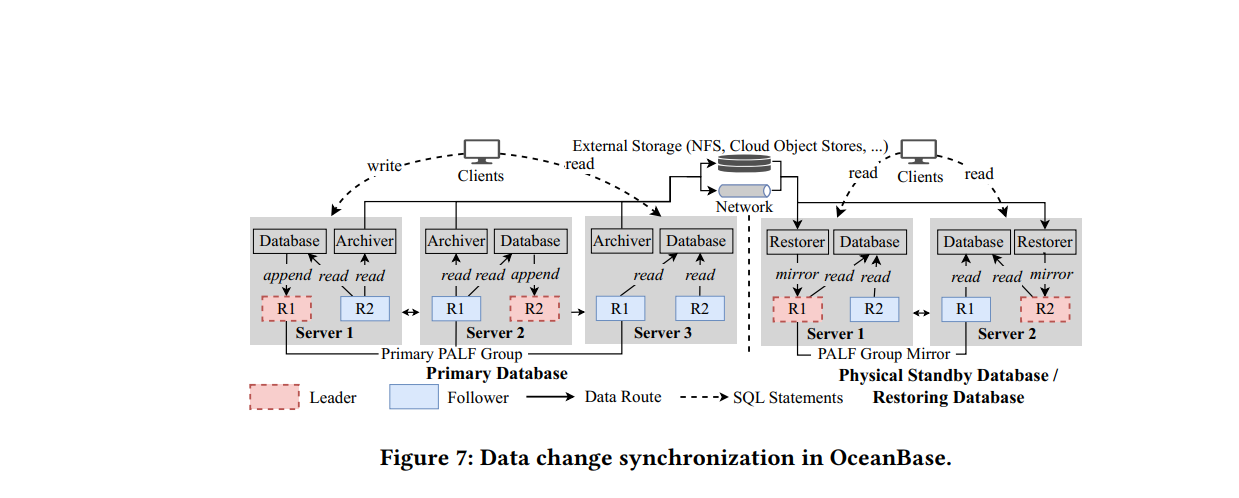
原文:
As shown in Figure 7, the physical standby database is an independent database in which the data are identical to the primary
database. It could serve part of read requests to relieve pressure
on the primary database. Compared to traditional primary-backup
architecture, it offers higher availability because each database cluster can tolerate failures. One of the most important features of the
physical standby database is database-level data protection and disaster recovery, a physical standby database can be switched to be
the primary database by a failover operation if the original primary
database becomes unavailable, which distinguish it from replicalevel protection such as Paxos learners [7]. In production databases,
database restore is a core component of the high-reliability feature.
If data have been lost due to storage media damage or human errors,
archived logs stored in offline storage (such as NFS or Cloud Object
Stores) could be used to restore an identical database
