#一、Overview
大家好, 本文主要描述是如何OceanBase 社区版实现一个 MySQL 5.7 新增的系统内建函数。
通过https://github.com/oceanbase/oceanbase/issues/1400 实践
开始时间:2023-6-8号–
思考 60秒,可能会产生下面几个疑问。
微行动:拆分到自己可用完成的步骤
-
新增一个表达式 ,需要修改parser模块吗? done
-
参考 https://github.com/boostorg/geometry/tree/develop 写一个 Boost.Geometry ExteriorRing 例子 done
-
todo-3:如何为Boost.Geometry ExteriorRing写一个单元测试。
-
了解boost库ExteriorRing 例子https://github.com/boostorg/geometry/blob/develop/test/core/ring.cpp,但是 ObGeoFuncAreaImpl 中这么多OB_GEO_GEOG_BINARY_FUNC_DEFAULT 宏是做用的。
二、 Solutions
通过例子学习
可以参考当前已有的实现,比如ST_area。
主要参考代码文件
ob_expr_st_area.cpp.h
ob_expr_st_area.h
ob_geo_func_area.cpp/.h
ob_geo_func_register.h
涉及文件:
- ob_sql.cpp:2425
- ob_dml_resolver.cpp:1589
- ob_select_resolver.cpp:1859
- ob_select_resolver.cpp:1274
sql 客户端
| ST_Area({poly |
mpoly}) |
计算多边形的面积,参数可以是Polygon或者MultiPolygon,MultiPolygon的面积是其中所有多边形面积的和 |
|
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/gis-polygon-property-functions.html#function_area
mysql> SET @poly =
'Polygon((0 0,0 3,3 0,0 0),(1 1,1 2,2 1,1 1))';
mysql> SELECT ST_Area(ST_GeomFromText(@poly));
+---------------------------------+
| ST_Area(ST_GeomFromText(@poly)) |
+---------------------------------+
| 4 |
+---------------------------------+
mysql> SET @mpoly =
'MultiPolygon(((0 0,0 3,3 3,3 0,0 0),(1 1,1 2,2 2,2 1,1 1)))';
mysql> SELECT ST_Area(ST_GeomFromText(@mpoly));
+----------------------------------+
| ST_Area(ST_GeomFromText(@mpoly)) |
+----------------------------------+
| 8 |
+----------------------------------+
|
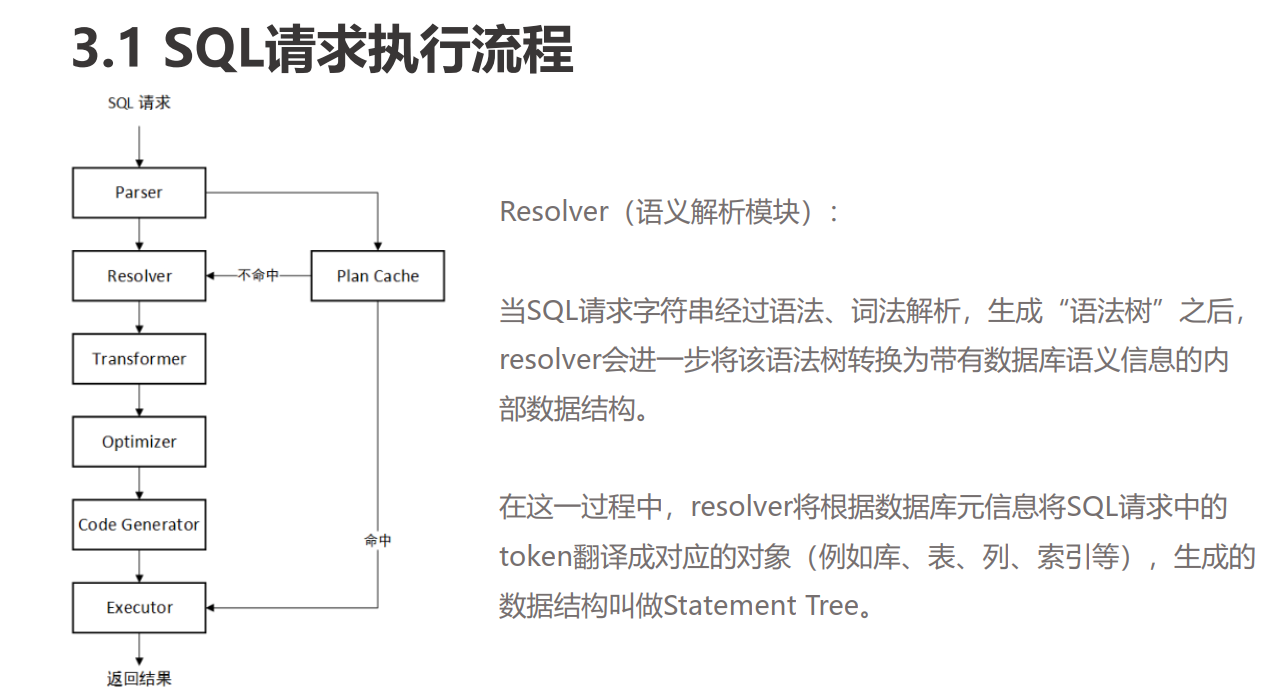
parser模块
表达式是如何被解析的
Parser 是整个 SQL 执行引擎的词法或语法解析器。通过flex( 词法分析器生成工具) 和bison(语法分析器生成器) 通过把 SQL 字符串解析为一个 ParseNode 组成的抽象语法树。
用法参考:miniob-sql-parser.md
相关代码:
-
ob_parser.cpp
-
sql_parser_mysql_mode.l
-
sql_parser_mysql_mode.y
resolver模块
ObDMLResolver::resolve_sql_expr
ObDMLResolver::resolve_sql_expr函数:
resolver模块
判断st_area函数是否存在
表达式解析类是位于sql/resolver/expr 的ObRawExprResolver,它输入ObParseNode 树,输出表达式树 ObRawExpr 。
这个 ObRawExpr 仅用于优化器阶段的语义分析优化,在生成物理执行计划后会被转换为为执行效率优化的 ObExpr 。
文件:D:\db\oceanbase\src\sql\resolver\expr\ob_raw_expr_resolver_impl.cpp
- 根据节点的类型:case T_FUN_SYS:,执行process_fun_sys_node和process_dll_udf_node(udf其他特殊类型的函数这里跳过)
- ObRawExprResolverImpl::process_fun_sys_node(const ParseNode *node, ObRawExpr *&expr)
在递归解析参数列表之前, 先检查下当前函数是否存在, 这是因为如果该函数报错 OB_ERR_FUNCTION_UNKNOWN, 外部会继续尝试是否是UDF、
- 根据函数名字查找类型type = ObExprOperatorFactory::get_type_by_name(func_name);
- ObExprOperatorType ObExprOperatorFactory::get_type_by_name(const ObString &name)
表达式注册
ob_expr_operator_factory.cpp ObExprSTArea函数是如何被注册的?
执行过程分析
-
ObExprSTArea op(alloc) //构造函数,虽然只有一个参数,但是继承关系,默认 函数名字和类型写死了。
-
表达式名字: st_area,表达式类型 T_FUN_SYS_ST_AREA 1676
#define N_ST_AREA “st_area”
T_FUN_SYS_ST_AREA = 1676,
sql 命令 关联函数执行
- REG_OP 实现是一个 lambda表达式,通过引用的方式捕获 获取外部变量:
其中 i ,alloc,NAME_TYPES 含义 表达式个数,分配器类型和全局静态数组
ObExprOperatorFactory::register_expr_operators()
- 对照代码 ObExprOperatorFactory::register_expr_operators()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
void ObExprOperatorFactory::register_expr_operators()
{
memset(NAME_TYPES, 0, sizeof(NAME_TYPES));
ObArenaAllocator alloc;
int64_t i = 0; //
REG_OP(ObExprSTArea);//注册表达式,这里面是lambda表达式
}
ObExprOperatorFactory::NameType ObExprOperatorFactory::NAME_TYPES[EXPR_OP_NUM] = { };
#define REG_OP(OpClass) \
do { //lambda 语法,[&] 按引用的方式捕获所有外部变量。 \
[&]() { \
OpClass op(alloc); // ObExprSTArea(common::ObIAllocator &alloc); \
if (OB_UNLIKELY(i >= EXPR_OP_NUM)) { \
LOG_ERROR("out of the max expr"); \
} else { \
NAME_TYPES[i].name_ = op.get_name(); \ //外部变量 位置register_expr_operators
NAME_TYPES[i].type_ = op.get_type(); \
NAME_TYPES[i].is_internal_ = op.is_internal_for_mysql(); \
OP_ALLOC[op.get_type()] = ObExprOperatorFactory::alloc<OpClass>; \
i++; //外部变量 位置register_expr_operators \
} \
}(); \
} while(0) //只执行一次就结束 理解成if
|
旁白:
- lambda本质就是 函数对象,在stl源码解析book有解释 函数对象:opeartor ()的一个类.
- lambda 语法,[&] 按引用的方式捕获所有外部变量。
- define是在预处理中进行替换,const语句是实实在在的编译器处理的
engine/expr
ObExprSTArea::eval_st_area是如何实现的
- 在ObExpr::EvalFunc g_expr_eval_functions 添加新的计算函数
ObExprSTArea::eval_st_area, /* 557 */
- ObExprSTArea::eval_st_area 函数
- 调用 Making Use of Boost Geometry in MySQL GIS
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
#define REG_SER_FUNC_ARRAY(id, array, size) \
static_assert(id >= 0 && id < OB_SFA_MAX, "too big id" #id); \
bool g_reg_ser_func_##id = ObFuncSerialization::reg_func_array( \
id, reinterpret_cast<void **>(array), size);
} // end namespace sql
|
geometry
- Why Boost.Geometry in MySQL?
1
2
3
|
computational geometry is not our field of expertise。
We evaluated multiple geometry libraries, and Boost.Geometry proved to fit our needs best.
http://mysql.taobao.org/monthly/2021/07/06/
|
-
GIS数据类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
GEOMETRY:不可实例化的数据类型,但是可以作为一个列的类型,存储任何一种其他类型的数据
POINT:点
LINESTRING:线
POLYGON:多边形,由多条闭合的线构成的图形
MULTIPOINT:点集合
MULTILINESTRING:线集合
MULTIPOLYGON:多边形集合
GEOMCOLLECTION:空间对象集合
|
-
GIS对象属性
MySQL中每个GIS对象都具有一些属性,MySQL中有一系列函数来获取GIS对象的属性,
类型(type):每个GIS对象都会有一个类型,表示了该对象是上述八种类型中的哪一种。
-
GIS数据格式
MySQL中支持WKT以及WKB两种格式来操作GIS数据,同时在内部以另外一种格式存储GIS数据。
WKT
即文本格式,在用户操作GIS类型的数据时可以使用直观的文本进行插入或查询,
MySQL支持OpenGIS定义的语法来写WKT数据,
示例如下:
WKT用文本的方式来表达Geometry,便于人的阅读。
WKT的格式为:Geometry类型(坐标数据)
Point:POINT(15 20)
LineString:LINESTRING(0 0, 10 10, 20 25, 50 60)
Polygon :POLYGON((0 0,10 0,10 10,0 10,0 0),(5 5,7 5,7 7,5 7, 5 5))
MultiPoint:MULTIPOINT(0 0, 20 20, 60 60)
MultiLineString:MULTILINESTRING((10 10, 20 20), (15 15, 30 15))
MultiPolygon:MULTIPOLYGON(((0 0,10 0,10 10,0 10,0 0)),((5 5,7 5,7 7,5 7, 5 5))) //??和Polygon 区别是?
参考:矢量空间数据格式
Polygon和MultiPolygon的结构较为复杂,概念相也容易混淆。Polygon和MultiPolygon都由多个环(Ring)构成的封闭的面状实体。

多面(MultiPolygon)
由多个相离的Polygon构成,并没有一个外环。

GeometryCollection:GEOMETRYCOLLECTION(POINT(1 -1), POINT(10 10), POINT(30 30), LINESTRING(15 15, 20 20))
WKB
该格式时OpenGIS定义的一个格式,使用二进制数据来保存信息,
例如平面坐标系下的点(1,-1)的WKB格式为:
0101000000000000000000F03F000000000000F0BF`
5.GIS函数
https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_63_0/libs/geometry/doc/html/geometry/reference/algorithms/area/area_2_with_strategy.html
GIS函数
MySQL提供了一系列的空间数据分析计算函数,大部分空间数据计算函数是基于Boost.Geometry库实现的,选择Boost的原因可以参考Manyi Lu的博客。
空间数据计算函数主要分为空间对象构造、空间数据格式转换、空间对象属性、空间对象关系计算,空间对象生成等等几大类
MySQL中GIS函数的实现定义在sql/item_geofunc*等文件中,其中大部分定义在sql/item_geofunc.h和sql/item_geofunc.cc文件中。
to_do
参考 https://github.com/boostorg/geometry/tree/develop 写一个 Boost.Geometry ExteriorRing 例子 下面是记录过程
| ST_ExteriorRing(poly) |
返回一个多边形对象的外圈,返回值是linestring(一条线),参数只能是polygon,否则报错或返回NULL |
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
https://github.com/boostorg/geometry/blob/develop/include/boost/geometry/core/exterior_ring.hpp
https://github.com/boostorg/geometry/blob/develop/test/core/ring.cpp
https://github.com/boostorg/geometry/blob/develop/include/boost/geometry/core/ring_type.hpp //type_traits
https://github.com/boostorg/geometry/blob/develop/include/boost/geometry/core/tags.hpp //GIS数据类型 是类标识,不是枚举值作用是什么?参考stl中的设计。
/workspaces/oceanbase/unittest/share/test_geo_func_difference.cpp
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
brief:该函数返回多边形的外环。
ingroup:该函数属于 exterior_ring 组。
note:该函数符合 OGC 标准,即符合开放地理空间联盟的标准。与 "ExteriorRing" 不同,该函数使用 "exterior ring"。
tparam:这是一个模板参数。Polygon 是将要从中获取外环的多边形的类型。
param:这是函数的参数。polygon 是将要从中获取外环的多边形的引用。
return:该函数返回一个指向外环的常量引用。
/*!
\brief Function to get the exterior ring of a polygon (const version)
\ingroup exterior_ring
\note OGC compliance: instead of ExteriorRing
\tparam Polygon polygon type
\param polygon the polygon to get the exterior ring from
\return a const reference to the exterior ring
\qbk{distinguish,const version}
*/
template <typename Polygon>
inline typename ring_return_type<Polygon const>::type exterior_ring(
Polygon const& polygon)
{
return core_dispatch::exterior_ring
<
typename tag<Polygon>::type,
Polygon const
>::apply(polygon);
}
|
小贴士:还是没看明白可用参考 看msyql 如何实现
第三部分:ST_ExteriorRing实现过程
新增一个函数相关文件
-
表达式和geo函数之间关系
- D:\db\oceanbase\deps\oblib\src\lib\geo\ob_geo_func_register.h
- deps/oblib/src/lib/geo/ob_geo_func_exterior_ring.cpp
-
geo函数实现
-
D:\db\oceanbase\deps\oblib\src\lib\CMakeLists.txt
-
D:\db\oceanbase\deps\oblib\src\lib\geo\ob_geo_func_exterior_ring.cpp
-
D:\db\oceanbase\deps\oblib\src\lib\geo\ob_geo_func_exterior_ring.h
- 新增一个函数实现
-
D:\db\oceanbase\src\sql\CMakeLists.txt
-
D:\db\oceanbase\src\sql\engine\expr\ob_expr_operator_factory.cpp
-
D:\db\oceanbase\src\sql\engine\expr\ob_expr_st_exterior_ring.cpp
-
D:\db\oceanbase\src\objit\include\objit\common\ob_item_type.h
-
D:\db\oceanbase\deps\oblib\src\lib\ob_name_def.h
-
D:\db\oceanbase\src\sql\resolver\expr\ob_raw_expr.h
-
D:\db\oceanbase\src\sql\engine\expr\ob_expr_eval_functions.cpp
单元测试
-
D:\db\oceanbase\unittest\share\CMakeLists.txt
如何提交pr
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
# 1. 关联远程仓库,保证代码可以和远程更新和提交
git remote add oceanbase https://github.com/oceanbase/oceanbase.git
git remote -v
# 2. oceanbase代码更新后更新自己仓库
自己在github 界面上 同步 然后pull
# 3. 提交分支到远程自己仓库
git push <远程主机名> <本地分支名>:<远程分支名>
# 从将本地的分支版本上传到远程参考(这里不是pr提交)
git push origin issue_1400:issue_1400
# 4. 界面上 提交pr
# 5. 可选
git push --set-upstream origin issue_1400
origin 是默认的远程版本库名称
等价于git push origin issue_1400:issue_1400
如果你用Windows就设置全局变量
git config --global core.autocrlf true
如果是mac/linux则设置
git config --global core.autocrlf input
如果使用 set list 显示隐藏字符 : set nolist :不显示
合并到master
git checkout master
#把本地分支合并到master
git merge issue_1400
手工修改
当Git无法自动合并分支时,就必须首先解决冲突。解决冲突后,再提交,合并完成
git add xxx
git commit -m "merged from main"
继续
git merge issue_1400
已经是最新的。
|
如何测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
|
# DEBUG 构建
bash build.sh debug --init
# 这里没有制作镜像,之间覆盖4.0版本的
echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
tiup cluster stop watchpoints //关闭其他的
tiup cluster disable watchpoints //关闭其他的
# 制作本地镜像
make DESTDIR=./ install &&
obd mirror create -n oceanbase-ce -V 4.2.0.1 -p ./usr/local -t my-oceanbase
Package ok
name: oceanbase-ce
version: 4.2.0.1
release:20230615110800
arch: x86_64
md5: dd828bcc94f6f4257d212bc73f7cbc42
Trace ID: d5ee1980-0b29-11ee-a4c9-000c29378c15
# 离线安装部署,禁用远程仓库
obd mirror disable remote
配置文件:
[root@localhost oceanbase]# cat mini-local-example.yaml
oceanbase-ce:
tag: my-oceanbase
servers:
# Please don't use hostname, only IP can be supported
- 127.0.0.1
global:
# The working directory for OceanBase Database. OceanBase Database is started under this directory. This is a required field.
home_path: /mnt/ob/observer
# The directory for data storage. The default value is $home_path/store.
data_dir: /mnt/ob/data
# The directory for clog, ilog, and slog. The default value is the same as the data_dir value.
redo_dir: /mnt/ob/redo
# Please set devname as the network adaptor's name whose ip is in the setting of severs.
# if set severs as "127.0.0.1", please set devname as "lo"
# if current ip is 192.168.1.10, and the ip's network adaptor's name is "eth0", please use "eth0"
devname: lo
mysql_port: 2881 # External port for OceanBase Database. The default value is 2881. DO NOT change this value after the cluster is started.
rpc_port: 2882 # Internal port for OceanBase Database. The default value is 2882. DO NOT change this value after the cluster is started.
zone: zone1
cluster_id: 1
# please set memory limit to a suitable value which is matching resource.
memory_limit: 6G # The maximum running memory for an observer
system_memory: 1G # The reserved system memory. system_memory is reserved for general tenants. The default value is 30G.
datafile_size: 15G # Size of the data file.
log_disk_size: 10G # The size of disk space used by the clog files.
cpu_count: 4
production_mode: false
enable_syslog_wf: false # Print system logs whose levels are higher than WARNING to a separate log file. The default value is true.
enable_syslog_recycle: true # Enable auto system log recycling or not. The default value is false.
max_syslog_file_count: 4 # The maximum number of reserved log files before enabling auto recycling. The default value is 0.
# root_password: # root user password, can be empty
---------------------------------------------------------------
obd cluster destroy watchpoints //删除之前的,不要轻易执行
# 创建
obd cluster deploy watchpoints -c ./mini-local-example.yaml
obd cluster start watchpoints
Wait for observer init ok
+---------------------------------------------+
| observer |
+-----------+---------+------+-------+--------+
| ip | version | port | zone | status |
+-----------+---------+------+-------+--------+
| 127.0.0.1 | 4.2.0.0 | 2881 | zone1 | ACTIVE |
+-----------+---------+------+-------+--------+
obclient -h127.0.0.1 -P2881 -uroot -p'GC29IoH3V9NQk8hIM2yr' -Doceanbase -A
obd cluster edit-config watchpoints
obd cluster start watchpoints // 启动不了怎么办?
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/gis-polygon-property-functions.html#function_area
mysql> SET @poly =
'Polygon((0 0,0 3,3 0,0 0),(1 1,1 2,2 1,1 1))';
mysql> SELECT ST_Area(ST_GeomFromText(@poly));
+---------------------------------+
| ST_Area(ST_GeomFromText(@poly)) |
+---------------------------------+
| 4 |
+---------------------------------+
SELECT ST_ExteriorRing(ST_GeomFromText(@poly));
obclient [oceanbase]> SELECT ST_ExteriorRing(ST_GeomFromText(@poly));
+-----------------------------------------+
| ST_ExteriorRing(ST_GeomFromText(@poly)) |
+-----------------------------------------+
| 4 |
+-----------------------------------------+
> 画外音:走到这里说明 ST_ExteriorRing生效了,执行结果和ST_Area一样,是因为完全copy了ST_Area代码,下一步就是调用boost实现
mysql> SET @poly =
'Polygon((0 0,0 3,3 3,3 0,0 0),(1 1,1 2,2 2,2 1,1 1))';
mysql> SELECT ST_AsText(ST_ExteriorRing(ST_GeomFromText(@poly)));
+----------------------------------------------------+
| ST_AsText(ST_ExteriorRing(ST_GeomFromText(@poly))) |
+----------------------------------------------------+
| LINESTRING(0 0,0 3,3 3,3 0,0 0) |
+----------------------------------------------------+
|
单元测试
todo-3:如何为Boost.Geometry ExteriorRing写一个单元测试? 参考:test_geo_func_difference.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
1. cp test_geo_func_difference.cpp test_geo_func_exterior_ring.cpp
2. unittest\share\CMakeLists.txt 添加
3. 替换
sed -i 's/TestGeoFuncDifference/TestGeoFuncExte
riorRring/g' test_geo_func_exterior_ring.cpp
4. unittest/share/test_geo_func_exterior_ring.cpp
//
发现 ob 提供外环函数计算是不是不用boost提供接口了 bWkbGeogLinearRing& ObWkbGeogPolygon::exterior_ring() ,发现boost 返回的不是简单值,是一个对象的化,bWkbGeogLinearRing& ObWkbGeogPolygon::exterior_ring()用的模板,不行2个都试试吧
这个得做一些测试吧。boost肯定是对的吧,经过那么多测试。如果返回的数据类型跟预期不符,是否可以转换一下?
|
task3 ST_ExteriorRing(poly)
参考 https://github.com/boostorg/geometry/tree/develop 写一个 Boost.Geometry ExteriorRing 例子 下面是记录过程
| ST_ExteriorRing(poly) |
返回一个多边形对象的外圈,返回值是linestring(一条线),参数只能是polygon,否则报错或返回NULL |
|
|
boost::geometry
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
brief:该函数返回多边形的外环。
ingroup:该函数属于 exterior_ring 组。
note:该函数符合 OGC 标准,即符合开放地理空间联盟的标准。与 "ExteriorRing" 不同,该函数使用 "exterior ring"。
tparam:这是一个模板参数。Polygon 是将要从中获取外环的多边形的类型。
param:这是函数的参数。polygon 是将要从中获取外环的多边形的引用。
return:该函数返回一个指向外环的常量引用。
/*!
\brief Function to get the exterior ring of a polygon (const version)
\ingroup exterior_ring
\note OGC compliance: instead of ExteriorRing
\tparam Polygon polygon type
\param polygon the polygon to get the exterior ring from
\return a const reference to the exterior ring
\qbk{distinguish,const version}
*/
template <typename Polygon>
inline typename ring_return_type<Polygon const>::type exterior_ring(
Polygon const& polygon)
{
return core_dispatch::exterior_ring
<
typename tag<Polygon>::type,
Polygon const
>::apply(polygon);
}
https://github.com/boostorg/geometry/blob/develop/include/boost/geometry/core/exterior_ring.hpp
https://github.com/boostorg/geometry/blob/develop/test/core/ring.cpp
https://github.com/boostorg/geometry/blob/develop/include/boost/geometry/core/ring_type.hpp //type_traits
https://github.com/boostorg/geometry/blob/develop/include/boost/geometry/core/tags.hpp //GIS数据类型 是类标识,不是枚举值作用是什么?参考stl中的设计。
/workspaces/oceanbase/unittest/share/test_geo_func_difference.cpp
https://github.com/watchpoints/master-cpp/blob/main/example/Boost/demo.cpp
https://github.com/boostorg/geometry/blob/develop/test/core/ring.cpp
|
我在编译过程中遇到下面问题,看例子:为什么可用编译通过
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
// geography
OB_GEO_UNARY_FUNC_BEGIN(ObGeoFuncAreaImpl, ObWkbGeogPolygon, double)
{
INIT_SUCC(ret);
const ObSrsItem *srs = context.get_srs();
if (OB_ISNULL(srs))
{
ret = OB_ERR_NULL_VALUE;
LOG_WARN("srs is null", K(ret), K(g->get_srid()), K(g));
}
else
{
boost::geometry::srs::spheroid<double> geog_sphere(srs->semi_major_axis(), srs->semi_minor_axis());
boost::geometry::strategy::area::geographic<> area_strategy(geog_sphere);
const ObWkbGeogPolygon *geo = reinterpret_cast<const ObWkbGeogPolygon *>(g->val());
result = boost::geometry::area(*geo, area_strategy);
}
return ret;
}
https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_65_0/libs/geometry/doc/html/geometry/reference/algorithms/area/area_1.html
template<typename Geometry>
default_area_result<Geometry>::type area(Geometry const & geometry)
|
画外音:自己想很多原因,但是 没有想到结果是 boost::geometry::area(geo) 看走眼了,
但是很奇怪,明明是2个不同类型没有报错
1
2
3
|
ype area(Geometry const & geometry)
class ObWkbGeomMultiPolygon
这个通过带代码没有看清楚。
|
编译错误2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/oblib/src/lib/geo/ob_geo_func_exterior_ring.cpp:10 8:64: error: non-const lvalue reference to type 'double' cannot bind to a value of unrelated type 'oceanbase::common::ObGeometry *'
return ObGeoFuncExteriorRingImpl::eval_geo_func(gis_context, result);
^~~~~~
/mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/oblib/src/lib/geo/ob_geo_dispatcher.h:34:85: note: passing argument to parameter 'result' here
static inline int eval_geo_func(const common::ObGeoEvalCtx &gis_context, RetTy pe &result);
^
/mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/oblib/src/lib/geo/ob_geo_dispatcher.h:66:79: error : non-const lvalue reference to type 'oceanbase::common::ObGeometry *' cannot bi nd to a value of unrelated type 'double'
ret = Functype::template EvalTree<ObCartesianPoint> :: eval(g, context, re sult);
|
- 原因分析: SELECT ST_AsText(ST_ExteriorRing(ST_GeomFromText(@poly))); ST_ExteriorRing 返回的一个是 LINESTRING 对象,现有表达式类型 都是 字符串,json int 没有st对象的定义呢?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
int ObExprSTExteriorRing::calc_result_type1
ST_ExteriorRing() handles its arguments as described in the introduction to this section.
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/gis-polygon-property-functions.html#function_st-exteriorring
mysql> SET @poly =
'Polygon((0 0,0 3,3 3,3 0,0 0),(1 1,1 2,2 2,2 1,1 1))';
mysql> SELECT ST_AsText(ST_ExteriorRing(ST_GeomFromText(@poly)));
+----------------------------------------------------+
| ST_AsText(ST_ExteriorRing(ST_GeomFromText(@poly))) |
+----------------------------------------------------+
| LINESTRING(0 0,0 3,3 3,3 0,0 0) |
+----------------------------------------------------+
ObExprSTAsText::ObExprSTAsText
enum class ObGeoType
{
GEOMETRY = 0,
POINT = 1,
LINESTRING = 2,
POLYGON = 3,
MULTIPOINT = 4,
MULTILINESTRING = 5,
MULTIPOLYGON = 6,
GEOMETRYCOLLECTION = 7,
GEOTYPEMAX = 31, // 5 bit for geometry type in column schema,set max 31
};
|
参考
[1] http://mysql.taobao.org/monthly/2021/07/06/
[2] https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_55_0/libs/geometry/doc/html/geometry/reference/algorithms/area/area_1.html
[3] https://desktop.arcgis.com/zh-cn/arcmap/latest/manage-data/using-sql-with-gdbs/st-exteriorring.htm
【4】 https://monica.im/s/f3b3dbfc
【5】侯捷系列视频
https://github.com/ZachL1/Bilibili-plus
[6] https://blog.csdn.net/iLuoPu/article/details/124034790 阅读中—-阅读完成
[7] https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_55_0/libs/geometry/doc/html/geometry/reference/algorithms/sym_difference.html
https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_64_0/libs/geometry/doc/html/geometry/reference/access/exterior_ring/exterior_ring_1.html
阅读中-
[8] https://www.jianshu.com/p/67e474b507a0 postgis多边形去孔洞
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/62444917
慢慢来,多看、多问、多总结,肯定是可以攻克的。
文章地址:
http://localhost:1313/post/oceanbase/1-2023-05-28-add-fun
https://wangcy6.github.io/post/oceanbase/1-2023-05-28-add-fun
https://wangcy6.github.io/post/oceanbase/2022/oceanbase_day2/
沟通步骤
-
准备好一个ppt,在写代码之前演示最终目标 和架构设计 就是如何去实现的 【不要说公司部门环境不对 着就是最终结果,不要试着看看,一定是可以完全上线的项目,非demo和一个知识点。自己认为真的 不是闹着玩的。。】
一、这个技术出现的背景、初衷和要达到什么样的目标或是要解决什么样的问题
二、这个技术的优势和劣势分别是什么
三、这个技术适用的场景。任何技术都有其适用的场景,离开了这个场景
四、技术的组成部分和关键点。
五、技术的底层原理和关键实现
六、已有的实现和它之间的对比
-
经过领导,专家 进行鸡蛋里挑骨头。【自己做好了别人路了胡扯,不会对别人产生任何影响,做事和做人一样,无论熟悉人,还是老师,领导,不相关人 反对 他们反馈信号,接受质疑,经过九九八十一难考验,并且你还在坚持认为对的。】
-
最后融合别人建议,然后完善你项目。【不听老人言,吃亏在眼前,不敢接受别人批评,说明自己完全没有把握,才去否定 愤怒方式】
遇到的坑
编译1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
/mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/3rd/usr/local/oceanbase/deps/devel/include/boost/geometry/core/interior_type.hpp:95:68: error: no type named 'type' in 'boost::geometry::traits::interior_const_type<const oceanbase::common::ObWkbGeomPolygon *>'
typename traits::interior_const_type<nc_polygon_type>::type,
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~^~~~
/mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/3rd/usr/local/oceanbase/deps/devel/include/boost/geometry/core/interior_type.hpp:153:37: note: in instantiation of template class 'boost::geometry::core_dispatch::interior_return_type<boost::geometry::polygon_tag, const oceanbase::common::ObWkbGeomPolygon *const>' requested here
typedef typename core_dispatch::interior_return_type
^
/mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/3rd/usr/local/oceanbase/deps/devel/include/boost/geometry/core/interior_rings.hpp:135:17: note: in instantiation of template class 'boost::geometry::interior_return_type<const oceanbase::common::ObWkbGeomPolygon *const>' requested here
inline typename interior_return_type<Polygon const>::type interior_rings(
^
/mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/oblib/src/lib/geo/ob_geo_func_exterior_ring.cpp:81:10: note: while substituting deduced template arguments into function template 'interior_rings' [with Polygon = const oceanbase::common::ObWkbGeomPolygon *]
result= bg::interior_rings(geo);
^
/mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/oblib/src/lib/geo/ob_geo_func_exterior_ring.cpp:81:10: error: no matching function for call to 'interior_rings'
result= bg::interior_rings(geo);
^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/3rd/usr/local/oceanbase/deps/devel/include/boost/geometry/core/interior_rings.hpp:114:53: note: candidate template ignored: substitution failure [with Polygon = const oceanbase::common::ObWkbGeomPolygon *]
inline typename interior_return_type<Polygon>::type interior_rings(Polygon& polygon)
^
/mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/3rd/usr/local/oceanbase/deps/devel/include/boost/geometry/core/interior_rings.hpp:135:59: note: candidate template ignored: substitution failure [with Polygon = const oceanbase::common::ObWkbGeomPolygon *]
inline typename interior_return_type<Polygon const>::type interior_rings(
^
In file included from /mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/build_debug/deps/oblib/src/lib/CMakeFiles/oblib_lib.dir/Unity/unity_oblib_lib_geo/1_cxx.cxx:51:
/mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/oblib/src/lib/geo/ob_geo_func_exterior_ring.cpp:99:19: error: assigning to 'oceanbase::common::ObGeometry *' from incompatible type 'const oceanbase::common::ObWkbGeogLinearRing'
result = geo->exterior_ring();
~~~~~^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/oblib/src/lib/geo/ob_geo_func_exterior_ring.cpp:106:28: error: out-of-line definition of 'eval' does not match any declaration in 'oceanbase::common::ObGeoFuncExteriorRing'
int ObGeoFuncExteriorRing::eval(const ObGeoEvalCtx &gis_context, ObGeometry *&result)
^~~~
/mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/oblib/src/lib/geo/ob_geo_func_exterior_ring.cpp:108:64: error: non-const lvalue reference to type 'double' cannot bind to a value of unrelated type 'oceanbase::common::ObGeometry *'
return ObGeoFuncExteriorRingImpl::eval_geo_func(gis_context, result);
^~~~~~
/mnt/oceanbase/oceanbase/deps/oblib/src/lib/geo/ob_geo_dispatcher.h:34:85: note: passing argument to parameter 'result' here
static inline int eval_geo_func(const common::ObGeoEvalCtx &gis_context, RetType &result);
|



