【注意】最后更新于 August 7, 2024,文中内容可能已过时,请谨慎使用。
一、青铜:前端开发展示一个多级菜单(目录)
1.1 题目描述
树状结构或层次结构的数据在企业应用里非常常见,
例如公司的组织架构、文档库的目录结构、
仓库的库位组织以及物件的分类等等
如图:
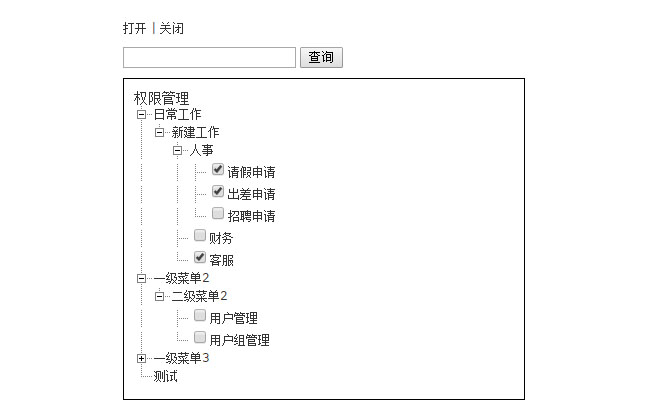
请设计一个表结构,存储多级菜单(目录)
1.2 采用什么数据结构表示?(数据库设计)
什么是邻接列表
邻接列表模型的特点是简单。
表中的每条记录都包含对其父级的引用,形成父子关系。
这通常是通过使用存储父节点标识符的列来实现的。
没有父节点的根节点通常由父列中的 NULL 值表示。
优点:
问题(在 SQL 查询中暴露):
例如:
| category_id |
parent_id |
category_name |
| 1 |
NULL |
Electronics |
| 2 |
1 |
Computers |
| 3 |
2 |
Laptops |
| 4 |
2 |
Desktops |
| 5 |
1 |
Televisions |
| 6 |
3 |
Gaming Laptops |
| 7 |
3 |
Business Laptop |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
//表结构
CREATE TABLE categories (
category_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
parent_id INT NULL,
category_name TEXT NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (parent_id) REFERENCES categories(category_id)
);
CREATE INDEX idx_categories_parent ON categories(parent_id);
//插入记录
INSERT INTO categories (category_id, category_name, parent_id) VALUES
(1, 'Electronics', NULL),
(2, 'Computers', 1),
(3, 'Laptops', 2),
(4, 'Desktops', 2),
(5, 'Smartphones', 1);
|
邻接列表优点
📌 为什么使用邻接表模型存储多级目录?
- 简单直观,开发与维护友好
- 插入、更新、删除操作高效
- 查询常见访问路径高效
个人感受:✔️ 为什么一般用 parent_id 而非 child_id?
- 多级目录或分类结构中,每个节点通常只有一个父节点,但可以有多个子节点
- 用
parent_id 的邻接表模型符合关系型数据库范式。若用 child_id,需定义多个子字段,容易违反第一范式(1NF),难以扩展,字段冗余严重
数据库设计三大范式
(1)简单归纳:
第一范式(1NF):字段不可分;
第二范式(2NF):有主键,非主键字段依赖主键;
第三范式(3NF):非主键字段不能相互依赖。
(2)解释:
1NF:原子性。 字段不可再分,否则就不是关系数据库;;
2NF:唯一性 。一个表只说明一个事物;
3NF:每列都与主键有直接关系,不存在传递依赖。
银行的面试官问了个简单的问题,满足第二范式,但是不满足第三范式的例子
第三范式定义:所有的非主属性(非主键)都直接由其它表的主属性(主键)推导生成,而不需要传递依赖。
重点:
1)满足第二范式。
2)不能传递依赖,非主属性不能部分或者传递依赖于码。
表: 学号, 姓名, 年龄, 学院名称, 学院电话
因为存在依赖传递: (学号) → (学生)→(所在学院) → (学院电话) 。
正确做法:
学生:(学号, 姓名, 年龄, 所在学院);
学院:(学院, 电话)。
邻接列表缺点
1. 深度遍历效率较差
要查询某个节点的所有后代(deep descendants)或完整路径,通常需要使用递归查询(如 CTE)或多次自连接。对于树深度较大时,查询非常复杂且性能低下。
“Finding all descendants of a node requires recursive queries or multiple joins”
2. 路径查询不便
想要查询某个节点从根节点到它的完整路径,需要多层连接并提前知道树深度,否则无法构造固定数量的自关联 JOIN。
“Before being able to see the full path … we have to know the level at which it resides.”
1.3 还有其他存储方式吗?
请参考:
- SQL反模式 第三章节 单 纯 的 树
- SQL Antipatterns. Naive Trees

二、白银:后端开发 请设计表示多级目录的类和相关接口
[!NOTE] 数据库的表要读取内存中去吧
如何在内存中表示
2.1 方式1 直接用指针表示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
class CategoryNode {
public:
int category_id; // 节点ID(主键)
std::string category_name; // 分类名称
CategoryNode* parent; // 指向父节点的指针(弱引用,避免循环强引用)
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<CategoryNode>> children; // 子节点列表
// 构造函数
CategoryNode(int id, const std::string& name, CategoryNode* parent_ptr = nullptr)
: category_id(id), category_name(name), parent(parent_ptr) {}
};
class CategoryTree {
private:
std::unique_ptr<CategoryNode> root; // 根节点
std::unordered_map<int, CategoryNode*> node_map; // ID到节点的映射(加速查找)
public:
// 添加节点(自动关联父子关系)
void add_node(int id, const std::string& name, int parent_id) {
CategoryNode* parent_ptr = (parent_id == -1) ? nullptr : node_map.at(parent_id);
auto new_node = std::make_unique<CategoryNode>(id, name, parent_ptr);
if (parent_ptr) {
parent_ptr->children.push_back(std::move(new_node));
} else { // 根节点
root = std::move(new_node);
}
node_map[id] = node_map.empty() ? root.get() : parent_ptr->children.back().get();
}
};
// 获取从根节点到当前节点的路径
std::vector<CategoryNode*> get_path(int id) {
std::vector<CategoryNode*> path;
CategoryNode* current = get_node(id);
while (current) {
path.push_back(current);
current = current->parent;
}
std::reverse(path.begin(), path.end()); // 从根到当前
return path;
}
// 查找所有后代节点(广度优先)
std::vector<CategoryNode*> get_descendants(int id) {
std::vector<CategoryNode*> result;
std::queue<CategoryNode*> queue;
queue.push(get_node(id));
while (!queue.empty()) {
auto current = queue.front();
queue.pop();
for (const auto& child : current->children) {
result.push_back(child.get());
queue.push(child.get());
}
}
return result;
}
|
2.2 从demo到产品化(CephFS)
🧩 CephFS 的目录树结构
🔹 Metadata Server(MDS)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
https://github.com/ceph/ceph/blob/main/src/mds/CInode.h
//MDS内部数据结构
class CInode {
inodeno_t ino;
snapid_t snapid;
std::map<std::string, CDentry*> dentries; // children
CInode* parent; // pointer to parent directory
};
//OpenFileTable 结构加速恢复:记录打开文件的路径信息,避免全量加载
CInode (根目录)
│
└── CDir (根目录内容)
├── CDentry ("a") ── CInode (目录"a")
│ │
│ └── CDir (目录"a"内容)
│ └── CDentry ("b.txt") ── CInode (文件"b.txt")
│
└── CDentry ("c") ── CInode (文件"c")
|
Ceph 文件系统由 MDS(Metadata Server)管理目录树结构,其内存模型核心由三种结构组成:
- CInode:表示每个文件或目录的
- CDentry:关联 inode 与其名称(目录项),支持同一个 inode 多个路径(硬链接);
- CDir:仅用于目录 inode,将该目录下所有 CDentry 组织起来。当目录被碎片化时,一个 CInode 可对应多个 CDir
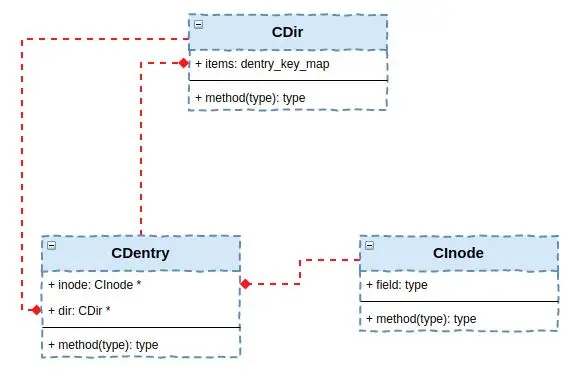
📌 结构特点
- 使用 C++ 类结构:父指针 + 子集合
- 更新目录、插入文件、递归遍历都在树结构上进行
-
- 动态扩展:目录过大时,
CDir 自动分片(如 10,000 文件/目录),新分片生成独立 CDir
- 持久化与恢复:
- 元数据通过 Journal 写入 RADOS 持久化。
- MDS 重启时,从 RADOS 加载元数据重建内存树。
- OpenFileTable 结构加速恢复:记录打开文件的路径信息,避免全量加载
| 数据结构 |
角色 |
关键作用 |
CInode |
元数据实体 |
存储文件/目录属性,指向数据块位置。 |
CDentry |
名称到实体的映射 |
链接文件名与 CInode,构建路径层级。 |
CDir |
目录内容容器 |
管理子项,支持分片以优化大规模目录性能。 |
三、如何体现左右子树(不体现)
没有左右子树的字段,因为目录结构是多叉树
四、Leetcode 588题
设计一个内存文件系统,模拟以下功能:
实现文件系统类:
FileSystem() 初始化系统对象List<String> ls(String path)void mkdir(String path) 根据给定的路径创建一个新目录。给定的目录路径不存在。如果路径中的中间目录不存在,您也应该创建它们。void addContentToFile(String filePath, String content)String readContentFromFile(String filePath) 返回 filePath下的文件内容。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
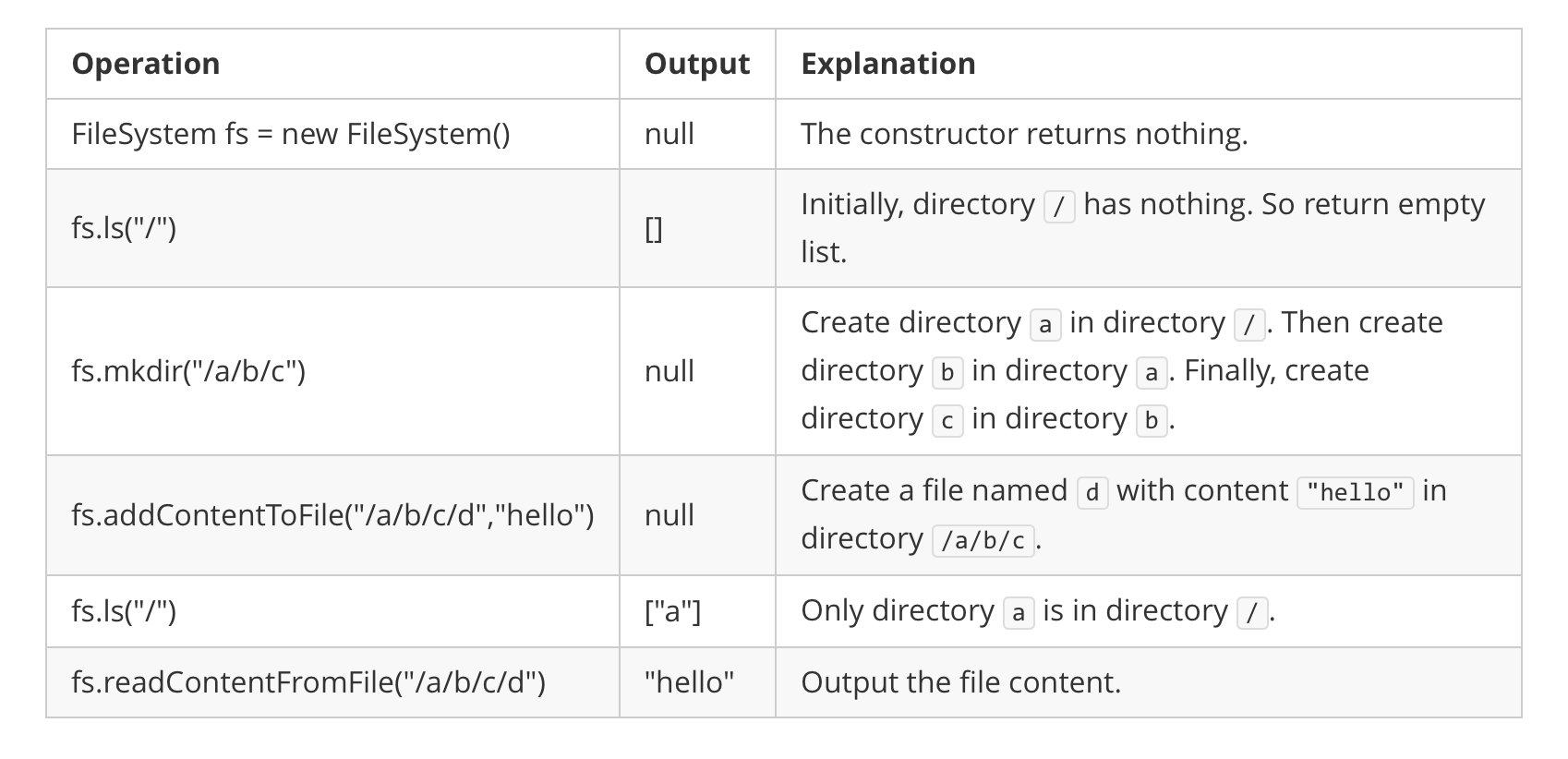
FileSystem fileSystem = new FileSystem();
fileSystem.ls("/"); // 返回 []
fileSystem.mkdir("/a/b/c");
fileSystem.addContentToFile("/a/b/c/d", "hello");
fileSystem.ls("/"); // 返回 ["a"]
fileSystem.readContentFromFile("/a/b/c/d"); // 返回 "hello"
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
|
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <set>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class FileSystem {
private:
// 文件系统节点结构
struct FileNode {
bool isFile = false; // 是否为文件
string content; // 文件内容
unordered_map<string, FileNode*> children; // 子节点映射
};
FileNode* root; // 根节点指针
// 分割路径为组成部分
vector<string> splitPath(const string& path) {
vector<string> parts;
if (path.empty() || path == "/") return parts;
istringstream iss(path);
string part;
while (getline(iss, part, '/')) {
if (!part.empty()) parts.push_back(part);
}
//
return parts;
}
// 根据路径查找节点
FileNode* traverse(const string& path) {
if (path == "/") return root;
vector<string> parts = splitPath(path);
FileNode* current = root;
for (const string& part : parts) {
if (!current->children.count(part)) return nullptr;
current = current->children[part];
}
return current;
}
public:
FileSystem() {
root = new FileNode(); // 初始化根节点
}
vector<string> ls(const string& path) {
FileNode* node = traverse(path);
if (!node) return {};
// 文件路径:返回文件名
if (node->isFile) {
int idx = path.find_last_of('/');
return {path.substr(idx + 1)};
}
// 目录路径:返回排序后的子项名称
vector<string> result;
for (const auto& child : node->children) {
result.push_back(child.first);
}
sort(result.begin(), result.end());
return result;
}
void mkdir(string path) {
vector<string> parts = splitPath(path);
FileNode* current = root;
for (const string& part : parts) {
if (!current->children.count(part)) {
current->children[part] = new FileNode();
}
current = current->children[part];
}
}
void addContentToFile(string filePath, string content) {
vector<string> parts = splitPath(filePath);
FileNode* current = root;
// 确保目录路径存在
for (int i = 0; i < parts.size() - 1; ++i) {
if (!current->children.count(parts[i])) {
current->children[parts[i]] = new FileNode();
}
current = current->children[parts[i]];
}
// 处理文件名
string fileName = parts.back();
if (!current->children.count(fileName)) {
current->children[fileName] = new FileNode();
current->children[fileName]->isFile = true;
}
current->children[fileName]->content += content;
}
string readContentFromFile(string filePath) {
FileNode* node = traverse(filePath);
if (node && node->isFile) {
return node->content;
}
return "";
}
};
|
1
|
std::istream& getline(std::istream& is, std::string& str, char delim);
|
其中,is 是输入流对象,str 是存储读取数据的字符串,delim 是指定的行分隔符(默认为换行符 \n)。
参考文章
- 如何在关系型数据库中存储树形结构
- What is Third Normal Form (3NF)?
参考数据
- SQL反模式 第三章 单 纯 的 树P29
- SQL Antipatterns. Naive Trees P34
最动人的作品,为自己而写,刚刚好打动别人
我在寻找一位积极上进的小伙伴,
一起参与神奇早起 30 天改变人生计划,发展个人事情,不妨 试试
1️⃣ 加入我的技术交流群Offer 来碗里 (回复“面经”获取),一起抱团取暖
 2️⃣关注公众号:后端开发成长指南(回复“面经”获取)获取过去我全部面试录音和大厂面试复盘攻略
2️⃣关注公众号:后端开发成长指南(回复“面经”获取)获取过去我全部面试录音和大厂面试复盘攻略
 3️⃣ 回复 面经 获取全部电子书
参考:# 分布式必读经典书籍
3️⃣ 回复 面经 获取全部电子书
参考:# 分布式必读经典书籍
抬头看天:走暗路、耕瘦田、进窄门、见微光,
- 我要通过技术拿到百万年薪P7职务,打通任督二脉。
- 但是不要给自己这样假设:别人完成就等着自己完成了,这个逃避问题表现,裁员时候别人不会这么想。
低头走路:
- 一次专注做好一个小事。
- 不扫一屋 何以扫天下,让自己早睡,早起,锻炼身体,刷牙保持个人卫生,多喝水 ,表达清楚 ,把基本事情做好。


 2️⃣关注公众号:后端开发成长指南(回复“面经”获取)获取过去我全部面试录音和大厂面试复盘攻略
2️⃣关注公众号:后端开发成长指南(回复“面经”获取)获取过去我全部面试录音和大厂面试复盘攻略
 3️⃣ 回复 面经 获取全部电子书
参考:# 分布式必读经典书籍
3️⃣ 回复 面经 获取全部电子书
参考:# 分布式必读经典书籍