c++编程思想
文章目录
【注意】最后更新于 December 2, 2019,文中内容可能已过时,请谨慎使用。
来源: c++编程思想(两卷合订本)
提问的方式
Q1 动态转换和静态转换的区别是什么?
小王第一次回答
一头雾水呀,平时没有自己用过,
唯一有印象的是写线程函数 传参采用 static_cast 从void* 类型转换到具体的类
dynamic_cast听名字跟virtual有关系,具体啥关系呢?
下面观点还是不对呢
-
static_cast 只能同类型转换,不能用于继承直接的类,不确定类之间的关系?
-
static_cast 不能用Downcasting转换?
-
对于个普通的cast,static_cast 可以采用Downcasting和dynamic_cast没有区别?
-
static_cast 不能用于virtual类型的转换
这样做有什么用呢?
- 和继承有关系 ,零星继承?
- 和对象模型有关系,定义和声明有关系?
评价:
混乱不清楚。别人区别是什么,你把平时各种观点,知识都拍出来,
没有做任何归纳总结区分。
小王二次回答
区别是,
static_cast 和dynamic_cast区别是在多重继承(主要菱形继承) Downcasting转换成转换成具体的实现类。
static_cast 在编译时时候无法确给出的基类指向具体实现类(同一个接口,被不同的是类实现),
dynamic_cast能区分出来
评价:首先自己都不清楚,然后说出啦模糊糊,罗哩罗嗦 别人更不懂了。虽然你是问题关键。
但是整体思路不清楚,不明白。这20%问题 不明白,剩余80不明白
小王第三次回答
区别 体现在downcast
-
static_cast 在编译节点能确定类与类之间有没有继承关系。检查出错误来 ,减少出错概率 【独有习惯】
dynamic_cast:采用运行时类型识别(RTTI),需要运行时候判断对错。编译器不容易发现错误。
(多重继承存在,2个类关系无法马上确定,因此不会报错)
首先推荐采用static_cast【 why why why 编译器来保证】
-
static_cast缺点来说 【dynamic_cast优点】
如果真实base指向结构和转换结构不同一个结构,
例如 基类转换成子类,继承同一个接口不同子类之间转换
static_cast依然转换成功,dynamic_cast能避免这个问题。
需要采用dynamic_cast【程序员来保证写代码正确】
If you guarantee the precondition, it’s fine.
If you don’t guarantee the precondition, then your code isn’t safe.
- 再有虚继承情况下 ,必须采用dynamic_cast 【独有习惯】
如果代码设计虚继承,采用动态,如果不涉及采用static_cast
If new_type is a pointer or reference to some class
Dand the type of expression is a pointer or reference to its non-virtual baseB,static_castperforms a downcast.This downcast is ill-formed if
Bis ambiguous, inaccessible, or virtual base (or a base of a virtual base) ofD.Such
static_castmakes no runtime checks to ensure that the object’s runtime type is actuallyD,(为什么不确定,这从对象模型来判断)and may only be used safely if this precondition is guaranteed by other means, such as when implementing static polymorphism.
Safe downcast may be done with
dynamic_cast.https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/static_cast
因为reinterpret_cast不能转换为vtable。
我寻找同样的疑问
Such
static_castmakes no runtime checks to ensure that the object’s runtime type is actuallyD,(
小王第三次理解
在有继承关键的类行向下转换上
(1) static_cast 在编译阶段,能根据判断定义类型 判断转换释放成立,编译器保证代码正确行
dynamic_cast 则不能
(2) dynamic_cast 对虚继承 能根据运行具体类型来识别
(3) 在安全上 static_cast依靠代码实现正确性,可能同一个接口不同类之间转换 可能转换成功。不提示错误。
Q2 map和hashmap的使用场景?
小王第一次理解:
-
都是key value类型 ,平时怎么用都可以,没有什么区别呀?, 虽然map有序,但是并没有使用这个功能
还是当作key value使用。不涉及范围查找呀
-
你回想在book ,map 就红黑树,hashmap就是桶呀 里面结构不一样,然后一个o(1) o(n) 扩容
然后这样100%别人不满意被pass?
- 这是stl提供结构,我直接用行了,区别是什么,各种优缺点什么,我不知道关键点在哪里呀?系统提供还有确定吗?
- 用法内部排序规则上。一个自定义函数对象来比较(有序),一个输入值随机的(无序)。但是平时也不怎么map做有序操作,key value
小王第一次回答:
内部数据结构不一样,一个红黑树,一个桶,遇到冲突元素时候桶通过链表来解决的。
然后时间复杂度不一样。和空间复杂度不一样
评价:
-
不要从内存角度考虑,对服务器来说 内存不是问题,能用钱解决的都不是事情,因为平时写代码不考虑内存问题,CPU 多核考虑?
-
更不要从好冲突考虑,如果冲突变成链表 这个你无法解决事情,引入更加复杂问题,排除这些因素干扰,
这人人想到。这个人人都知道。
小王第二次理解:
阅读文章
第1文章: ok耗时 45分钟
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hash_table
http://occcwiki.org/index.php/Data_Structures/Hash_Tables
https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-hans/%E5%93%88%E5%B8%8C%E8%A1%A8 [中文]
访问局部性 维基百科,自由的百科全书
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Locality_of_reference
http://www.xupifu.com/2017/01/19/cache-introduction/
缓存如何影响哈希
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CPU_cache
https://archive.siam.org/meetings/alenex05/papers/13gheileman.pdf
高级语言中的Map或Dictionary能否改写以利用局部性原理?
https://www.zhihu.com/question/28092327 [没看懂,知乎人太利好了]
7个示例科普CPU CACHEhttps://coolshell.cn/articles/10249.html[厉害,这个写清楚具体,看懂了]
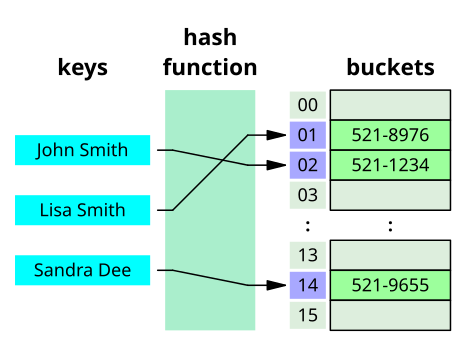
Advantages[edit]
-
The main advantage of hash tables over other table data structures is speed. This advantage is more apparent when the number of entries is large. Hash tables are particularly efficient when the maximum number of entries can be predicted in advance, so that the bucket array can be allocated once with the optimum size and never resized.
-
If the set of key-value pairs is fixed and known ahead of time (so insertions and deletions are not allowed), one may reduce the average lookup cost by a careful choice of the hash function, bucket table size, and internal data structures. In particular, one may be able to devise a hash function that is collision-free, or even perfect. In this case the keys need not be stored in the table.
Drawbacks[edit]
-
Although operations on a hash table take constant time on average, the cost of a good hash function can be significantly higher than the inner loop of the lookup algorithm for a sequential list or search tree. Thus hash tables are not effective when the number of entries is very small. (However, in some cases the high cost of computing the hash function can be mitigated by saving the hash value together with the key.)
hash因为hash计算和比较这2个操作,如果数量比较小情况下,不如o(n)循环快呢
-
For certain string processing applications, such as spell-checking, hash tables may be less efficient than tries, finite automata, or Judy arrays. Also, if there are not too many possible keys to store—that is, if each key can be represented by a small enough number of bits—then, instead of a hash table, one may use the key directly as the index into an array of values. Note that there are no collisions in this case.
在字符串处理方面,有更合适数据结构。例如前缀tree
-
The entries stored in a hash table can be enumerated efficiently (at constant cost per entry), but only in some pseudo-random order. Therefore, there is no efficient way to locate an entry whose key is nearest to a given key. Listing all n entries in some specific order generally requires a separate sorting step, whose cost is proportional to log(n) per entry. In comparison, ordered search trees have lookup and insertion cost proportional to log(n), but allow finding the nearest key at about the same cost, and ordered enumeration of all entries at constant cost per entry.
表示没看懂
-
If the keys are not stored (because the hash function is collision-free), there may be no easy way to enumerate the keys that are present in the table at any given moment.
表示没看懂
-
Although the average cost per operation is constant and fairly small, the cost of a single operation may be quite high. In particular, if the hash table uses dynamic resizing, an insertion or deletion operation may occasionally take time proportional to the number of entries. This may be a serious drawback in real-time or interactive applications.
在插入和删除过程中,引起扩容操作,引起单次查找耗时比较长,不是o(1),在试试交互情况有影响。
平均 不是 每一个。是实时交互方面很大的缺点。致命的缺点
,在需要有序性或者对单次查询有时间要求的应用场景下,应使用map,其余情况应使用unordered_map。
- Hash tables in general exhibit poor locality of reference—that is, the data to be accessed is distributed seemingly at random in memory. Because hash tables cause access patterns that jump around, this can trigger microprocessor cache misses that cause long delays. Compact data structures such as arrays searched with linear search may be faster, if the table is relatively small and keys are compact. The optimal performance point varies from system to system.
Hash tables in general exhibit poor locality of reference hash理解成动态数组来存储。实现一级存储
-
Hash tables become quite inefficient when there are many collisions.
在冲突情况下,效率低下
Ordered retrieval issue
Hash tables store data in pseudo-random locations, so accessing the data in a sorted manner is a very time consuming operation. Other data structures such as self-balancing binary search trees generally operate more slowly (since their lookup time is O(log n)) and are rather more complex to implement than hash tables but maintain a sorted data structure at all times. See a comparison of hash tables and self-balancing binary search trees.
Problems with hash tables
Although hash table lookups use constant time on average, the time spent can be significant. Evaluating a good hash function can be a slow operation. In particular, if simple array indexing can be used instead, this is usually faster.
Hash tables in general exhibit poor locality of reference—that is, the data to be accessed is distributed seemingly at random in memory. Because hash tables cause access patterns that jump around, this can trigger microprocessor cache misses that cause long delays. Compact data structures such as arrays, searched with linear search, may be faster if the table is relatively small and keys are cheap to compare, such as with simple integer keys. According to Moore’s Law, cache sizes are growing exponentially and so what is considered “small” may be increasing. The optimal performance point varies from system to system; for example, a trial on Parrot shows that its hash tables outperform linear search in all but the most trivial cases (one to three entries).
More significantly, hash tables are more difficult and error-prone to write and use. Hash tables require the design of an effective hash function for each key type, which in many situations is more difficult and time-consuming to design and debug than the mere comparison function required for a self-balancing binary search tree. In open-addressed hash tables it’s even easier to create a poor hash function.
Additionally, in some applications, a black hat with knowledge of the hash function may be able to supply information to a hash which creates worst-case behavior by causing excessive collisions, resulting in very poor performance (i.e., a denial of service attack). In critical applications, either universal hashing can be used or a data structure with better worst-case guarantees may be preferable. For details, see Crosby and Wallach’s Denial of Service via Algorithmic Complexity Attacks.
第2文章
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20170244/why-not-use-hashing-hash-tables-for-everything/20170281
hash这么好,为什么计算不全部都用它表示呢?
HashTable in general exhibit poor locality of reference that is, the data to be accessed is distributed seemingly at random in memory.
In what cases would it get to O(n)?
if you have such a bad hash function which produces the same hash value for all input stirngs (i.e. produce collisions)…
What container should I have chosen, map or unordered_map?
It is always the questions of requirements and kind/amount of data do you have.
When does a map get more time efficient than unordered_map?
It is just different structures. You’d better to make a chiose to use one of them depending on your typical use cases (takeing in account what kind of data do you have and its amount)
Does it hppaen when n is small?
In case of small data amount everything depends on particular STL implementation… So sometimes even a plain vector/array could be faster than associative containers…
第三个文章 其他语言对比
https://dave.cheney.net/2018/05/29/how-the-go-runtime-implements-maps-efficiently-without-generics
https://engineering.fb.com/developer-tools/f14/
不明白地方:
在删除相应的键之前,哈希表中的键和值的引用和指针必须保持有效
https://leveldb-handbook.readthedocs.io/zh/latest/cache.html
https://github.com/rockeet/nark-hashmap
小王第二次回答
Q2 class b,a(b), a=b 发生了什么? Assignment operator (C++)






辟谣:
- https://my.oschina.net/yepanl/blog/1588421 C++拷贝构造函数和拷贝赋值运算符 说法有错误的 不是分开的。
如果分开的看,肯定有问题的
Q3 new 原理是什么?
小王第一次回答(被重复问过3次 动态数组,vector )
被重复问过3次 ,1个月之后,回到当初错误理解上,被别人KO ,问题重点是什么不清楚,你牢牢记住过去记忆内容?别人参考和单纯 就是 c++ 课本上基本理论,你扩展操作系统,原理什么概念解释 他们一脸蒙蔽
c++ new 1 申请内存 2 调用构造函数
c++ delte 1 调用构造函数 2 释放内存
小王是这样想的
我感觉用内存池,里面提前申请,小内存,大内存,划分接线不清楚,大小不清楚
小王二次回答(弄清楚里tree结构的关系每个节点术语?)
小王收到第一次反馈:
画外音:
【你像别人介绍内存池原理,虚拟内存原理,里面各种知识点?你说半天别人根本不知道说什么,别人说根本不懂】 !!!
| TCMalloc | ||
| jmalloc | ||
| glibc |
参考
https://wetest.qq.com/lab/view/318.html?from=content_testerhome
https://www.zhihu.com/question/302440083
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/29216091
http://gao-xiao-long.github.io/2017/11/25/tcmalloc/
https://github.com/selfboot/CS_Offer/blob/master/Linux_OS/StackHeap.md
https://docs.huihoo.com/ace_tao/ACE-2002-12/Part-Two/Chapter-3.htm
https://my.oschina.net/zengjs275/blog/1068850
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_a459dcf50101692b.html
Q4 什么是虚函数?(被重复问过3次 ,过一段时间,回到当初错误理解上)?
被重复问过3次 ,1个月之后,回到当初错误理解上,被别人KO ,问题重点是什么不清楚,你牢牢记住过去记忆内容?别人参考和单纯 就是 c++ 课本上基本理论,你扩展操作系统,原理什么概念解释 他们一脸蒙蔽
