操作系统入门知识--网络
文章目录
【注意】最后更新于 April 23, 2022,文中内容可能已过时,请谨慎使用。
day1
:请一定要有自信。你就是一道风景,没必要在别人风景里面仰视。
问题:直觉
为了快速掌握本文所要表达的思想,我们可以带着以下问题阅读。
-
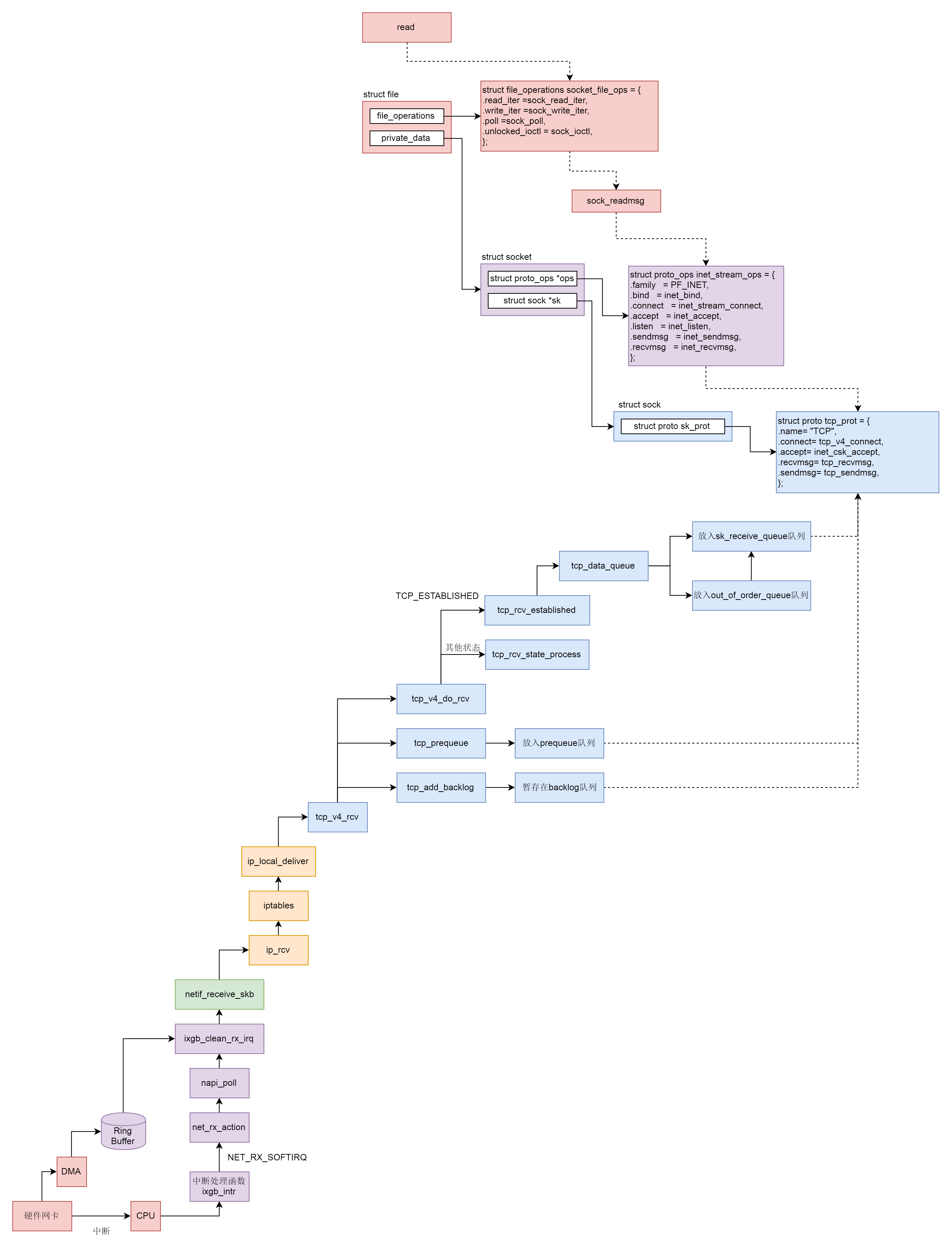
linux的sysctl系统参数中,有类似tcp_low_latency这样的开关,默认为0或者配置为1时是如何影响TCP消息处理流程的?
-
问: 一个网络包了,会触发一次中断处理程序,10000个网络包来了,触发100000次中断吗?是不是太频繁了呢
-
应用程序开始收取TCP消息,与程序所在的机器网卡上接收到网络里发来的TCP消息,这是两个独立的流程。它们之间是如何互相影响的?
例如,应用程序正在收取消息时,内核通过网卡又在这条TCP连接上收到消息时,究竟是如何处理的?
若应用程序没有调用read或者recv时,内核收到TCP连接上的消息后又是怎样处理的?
-
linux的sysctl系统参数中,有类似tcp_low_latency这样的开关,默认为0或者配置为1时是如何影响TCP消息处理流程的?
-
资料:第一手资料
同样看资料,你为什么不去看成功人怎么走的
因为看他们文章你离开舒适区 难。
看八股文 跟不没理解人写文章 简单 迷糊
大v—陶辉
大v–Torvalds
- 2017年Torvalds 提交 epoll: Add busy poll support to epoll with socket fds. commit
林纳斯·本纳第克特·托瓦兹(Linus Benedict TorvaldsLinux内核](https://baike.baidu.com/item/Linux内核/10142820)的发明人及该计划的合作者
epoll: Add busy poll support to epoll with socket fds.
- Busy Polling: Past, Present, Future https://legacy.netdevconf.info/2.1/papers/BusyPollingNextGen.pdf
- https://legacy.netdevconf.info/2.1/slides/apr6/dumazet-BUSY-POLLING-Netdev-2.1.pdf
- 从NAPI说一说Linux内核数据的接收流程
- busy_poll 设计
-
NAPI Mechanism
代码:
理解
https://legacy.netdevconf.info/2.1/slides/apr6/dumazet-BUSY-POLLING-Netdev-2.1.pdf
句子5;
SO_BUSY_POLL is a socket option, that allows precise enabling of busy polling,
|
|
理解:
,同样一个网络包要在三个主体之间交接。
-
句子4:
Traditional Model, how does it work ?
|
|
- 句子3:
Conference 2012 [1], busy polling has been first defined as the ability for user thread waiting for some incoming network message to directly poll the device ring buffer, instead of traditional way of waiting on a socket receive buffer being feeded by nomal RX handling.
翻译3
socket隔离了用户进程和协议栈,RX/TX queue隔离了协议栈和设备驱动
隔离有隔离的好处,但也有坏处!!目前存在一种 突破这种隔离的方法,让socket直接深入到设备层直接poll skb!!注意,这是一个poll操作,并不是让socket直接处理协议栈流程。
socket直接poll的意思是说,socket在队列中没有读到数据包的时候,并不是睡眠,然后等待NET RX内核线程将数据包放入队列后将其唤醒,而是直接去问设备:现在有数据包吗?如果有,我直接带走它们去协议栈,而不需要你送它们去了。
这是一种“拉”的方式,而不是以往的那种“推”的方式,拉和推的区别在于,对于接收者,拉是同一个实体,是主动的,而推则是被动的。
- Linux NAPI
Linux NAPI model added a generic layer helping both throughput and fairness among devices, at the cost of jitter. Busy Polling was added in 2013 as an alternative model where user application thread was opportunistically going to poll the device, burning cycles and potentially avoiding the interrupts latencies.
Linux NAPI 模型添加了一个通用层,帮助两者 设备之间的吞吐量和公平性,以抖动为代价。 Busy Polling 于 2013 年作为替代模型添加,其中 用户应用程序线程机会主义地轮询 设备,燃烧周期,并可能避免中断 延迟。
- no device interrupts
By no longer waiting for device interrupts being generated/handled, and polling driver/device queues, we can avoid context switches, keep CPU in C0 state, and immediately react to packet arrival, on the proper cpu (regardless of CPU IRQ affinities) Idea was to let the application thread calling a recv() system call or any other socket call that would normally have to wait for incoming messages directly call a new device driver method and pull packets. This would be done in a loop, bounded by a variable time budget
通过不再等待设备中断产生/处理,轮询驱动程序/设备队列,我们可以避免 上下文切换,将 CPU 保持在 C0 状态,并在正确的 cpu 上立即对数据包的到达做出反应(无论 CPU IRQ 亲和性) 想法是让应用程序线程调用 recv() 系统调用或任何其他通常必须调用的套接字调用 等待传入消息直接调用新的设备驱动程序 方法和拉数据包。 这将在一个循环中完成, 受可变时间预算的限制
SO_BUSY_POLL is a socket option, that allows precise enabling of busy polling,
In linux-4.12, epoll()[9] support was added by Sridhar Samudrala and Alexander Duyck, with the assumption that an application using epoll() and busy polling would first make sure that it would classify sockets based on their receive queue (NAPI ID), and use at least one epoll fd per receive queue. SO_INCOMING_NAPI_ID was added as a new socket option to retrieve this information, instead of relying on other mechanisms (CPU or NUMA identifications).
在 linux-4.12 中,Sridhar Samudrala 和 Alexander Duyck 添加了对 epoll()[9] 的支持,假设使用 epoll() 和繁忙轮询的应用程序将首先确保 它将根据套接字的接收队列对套接字进行分类 (NAPI ID),并且每个接收队列至少使用一个 epoll fd。 SO_INCOMING_NAPI_ID 作为新的套接字选项添加到 检索此信息,而不是依赖其他机制(CPU 或 NUMA 标识)。
- 类似生产者 消费者设计
socket隔离了用户进程和协议栈,RX/TX queue隔离了协议栈和设备驱动
隔离有隔离的好处,但也有坏处!!目前存在一种 突破这种隔离的方法,让socket直接深入到设备层直接poll skb!!注意,这是一个poll操作,并不是让socket直接处理协议栈流程。
socket直接poll的意思是说,socket在队列中没有读到数据包的时候,并不是睡眠,然后等待NET RX内核线程将数据包放入队列后将其唤醒,而是直接去问设备:现在有数据包吗?如果有,我直接带走它们去协议栈,而不需要你送它们去了。
这是一种“拉”的方式,而不是以往的那种“推”的方式,拉和推的区别在于,对于接收者,拉是同一个实体,是主动的,而推则是被动的。
epoll: Add busy poll support to epoll with socket fds.
This patch adds busy poll support to epoll.
The implementation is meant to be opportunistic in that it will take the NAPI ID from the last socket that is added to the ready list that contains a valid NAPI ID and it will use that for busy polling until the ready list goes empty.
- Once the ready list goes empty the NAPI ID is reset and busy polling is disabled until a new socket is added to the ready list
.4. In addition when we insert a new socket into the epoll we record the NAPI ID and assume we are going to receive events on it. If that doesn’t occur it will be evicted as the active NAPI ID and we will resume normal behavior. An application can use SO_INCOMING_CPU or SO_REUSEPORT_ATTACH_C/EBPF socket options to spread the incoming connections to specific worker threads based on the incoming queue. This enables epoll for each worker thread to have only sockets that receive packets from a single queue.
- So when an application calls epoll_wait() and there are no events available to report, busy polling is done on the associated queue to pull the packets.
Busy polling was tested for TCP and connected UDP sockets, using standard system calls : recv() and friends , poll() and select()
理解翻译:
-
如果没有可读写socket,busy polling 一直在轮训。 epoll_wait
epoll_wait–>do_epoll_wait–>ep_poll—>—ep_poll_callback—ep_send_events_proc–to call f_op->poll().
在任何情况下使用spin_lock_irq都是安全的。因为它既禁止本地中断,又禁止内核抢占
若有就绪则直接将 事件和fd返回给用户空间,没有就绪的话先把自己调度出去,然后等待socket那边有事件后通过 回调 ep_poll_callback()来唤醒。
the incoming connections
New API (also referred to as NAPI) is an interface to use interrupt mitigation techniques for networking devices in the Linux kernel. Such an approach is intended to reduce the overhead of packet receiving. T
he idea is to defer incoming message
新 API(也称为 NAPI)是在 Linux 内核中为网络设备使用中断缓解技术的接口。 这种方法旨在减少数据包接收的开销。 这个想法是推迟传入的消息
What Does “Busy Waiting” Mean in Operating Systems?
|
|
- 设计模式之访问者模式
https://juejin.cn/post/6844903582056054791 ✅
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1755832 ✅
单词:
overhead of packet receiving.
approach
https://www.zhihu.com/question/66733477
首先了解自旋。什么是自旋(spin)呢?更为通俗的一个词是『忙等待』(busy waiting)。最最通俗的一个理解,其实就是死循环……
5
因此,当应用程序调用 epoll_wait() 并且没有可报告的事件时,会在关联队列上进行繁忙轮询以拉取数据包。
|
|
calls:
pull :
available
- 轮询
NAPI 是 Linux 上采用的一种提高网络处理效率的技术,它的核心概念就是不采用中断的方式读取数据,而代之以首先采用中断唤醒数据接收的服务程序,然后 POLL 的方法来轮询数据
目前 NAPI 技术已经在网卡驱动层和网络层得到了广泛的应用
翻译:
同步和异步的主要区别在于数据从内核缓冲区 -> 用户内存这个过程需不需要用户进程等待。
等待内核态准备数据结束之后,会自动回通知用户态的线程进行读取信息数据,此时之前用户态的线程不需要等待,可以去做其他操作。
-
在non-blocking IO中,虽然进程大部分时间都不会被block,但是它仍然要求进程去主动的check,并且当数据准备完成以后,也需要进程主动的再次调用recvfrom来将数据拷贝到用户内存。
-
asynchronous IO则完全不同。它就像是用户进程将整个IO操作交给了他人(kernel)完成,然后他人做完后发信号通知。在此期间,用户进程不需要去检查IO操作的状态,也不需要主动的去拷贝数据。
【1 马上返回 不考虑处理情况】从kernel的角度,当它受到一个asynchronous read之后,首先它会立刻返回,所以不会对用户进程产生任何block。
【2 让其他人处理】kernel会等待数据准备完成,然后将数据拷贝到用户内存,当这一切都完成之后,kernel会给用户进程发送一个signal,告诉它read操作完成了。
- 例子: 懒人:鱼 自己从河里跳出来。
|
|
-
Java 中的 IO 模型 vs IO 模型
-
BIO、NIO、AIO
-
类似Redis、NodeJS这样的单进程、单线程高并发服务,只能向分布式集群方向发展,才能继续提升性能。
-
Nginx通过Master/Worker多进程架构,可以充分使用服务器上百个CPU核心,实现C10M。
-
sysctl_tcp_low_latency 哪里体现低延迟了。原来怎么解决延迟的。【队列作用 不完全处理完毕 尽快结束 ,下次子处理】
如果 sysctl_tcp_low_latency 设置为 1,也即没有 prequeue 队列,或者 prequeue 队列为空,则需要处理 backlog 队列,在 release_sock 函数中处理。
解决问题:
流程图:
