【注意】最后更新于 May 13, 2020,文中内容可能已过时,请谨慎使用。
问题: reids成为后端开发人员必备技能,你对他了解多少?
像电信公司 根本不用redis,其他公司之间拿过来使用 满足业务了,
你改如何学习,很简单从源码和特性这2个角度。
然后思考为什么这样设计?动手目的只是验证的想法。
版本
最新特性是什么
| 版本 |
发布日期 |
其中一个特性 |
| Redis2.8 |
2013年11月22 |
一个key的类型和编码类型是什么? |
| Redis3.0(里程碑) |
2015年4月1日 |
集群方案是什么 |
| Redis5.0 |
2018年10月17 |
|
| Redis6.0 |
|
多线程 |
源码阅读参考
目录索引
- 一个key的类型和编码类型是什么?
- redis集群方案
第一天 what is Redis
学习资料
目标:
Redis Cluster goals
Redis Cluster is a distributed implementation of Redis with the following goals, in order of importance in the design:
- High performance and linear scalability up to 1000 nodes. There are no proxies, asynchronous replication is used, and no merge operations are performed on values.
最高扩展到1000个节点,拿到不能超过吗、为什么这样说
-
Acceptable degree of write safety: the system tries (in a best-effort way) to retain all the writes originating from clients connected with the majority of the master nodes. Usually there are small windows where acknowledged writes can be lost. Windows to lose acknowledged writes are larger when clients are in a minority partition.
-
Availability: Redis Cluster is able to survive partitions where the majority of the master nodes are reachable and there is at least one reachable slave for every master node that is no longer reachable. Moreover using replicas migration, masters no longer replicated by any slave will receive one from a master which is covered by multiple slaves.
学习输出
#1 陈咬金第一斧 模型什么
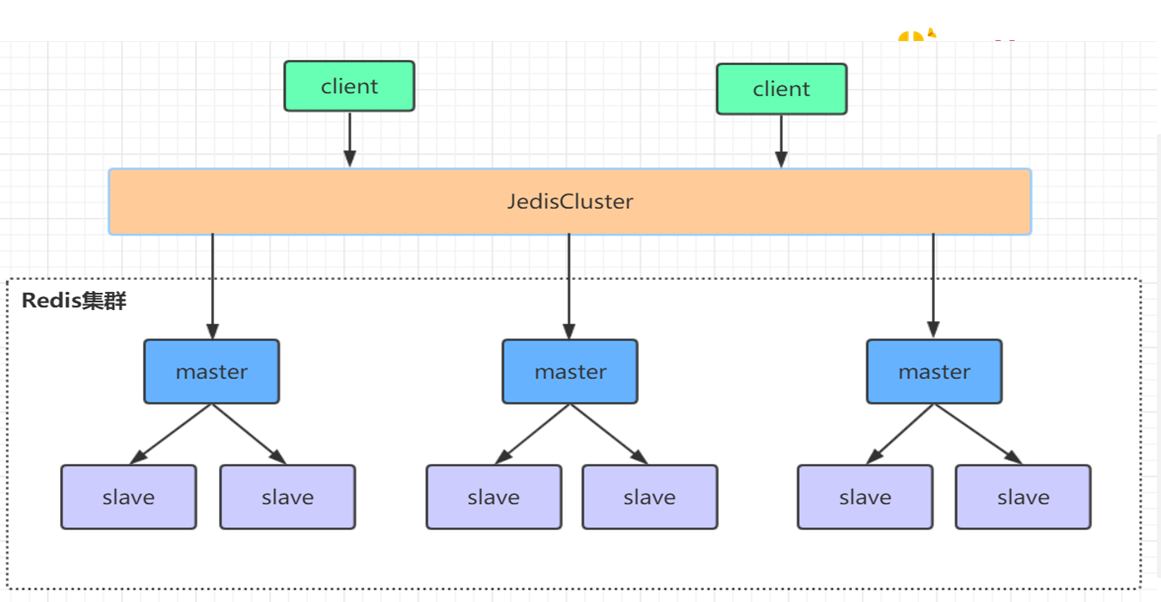
#2 陈咬金第二斧 数据状态是什么
1 FAIL状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
A PFAIL condition is escalated to a FAIL condition when the following set of conditions are met:
Some node, that we'll call A, has another node B flagged as PFAIL.
Node A collected, via gossip sections, information about the state of B from the point of view of the majority of masters in the cluster.
The majority of masters signaled the PFAIL or FAIL condition within NODE_TIMEOUT * FAIL_REPORT_VALIDITY_MULT time. (The validity factor is set to 2 in the current implementation, so this is just two times the NODE_TIMEOUT time).
If all the above conditions are true, Node A will:
Mark the node as FAIL.
Send a FAIL message to all the reachable nodes.
|
2 slave 发起投票条件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
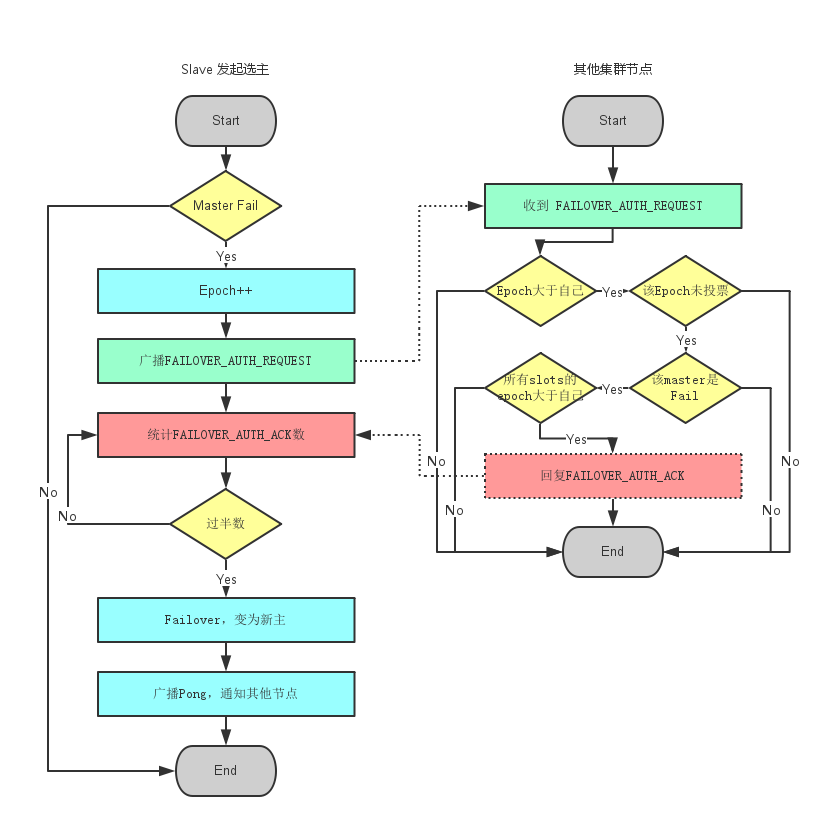
于挂掉的master可能会有多个slave,从而存在多个slave竞争成为master节点的过程, 其过程如下:
1.slave发现自己的master变为FAIL
2.将自己记录的集群currentEpoch加1,并广播FAILOVER_AUTH_REQUEST信息
3.其他节点收到该信息,只有master响应,判断请求者的合法性,并发送FAILOVER_AUTH
4.尝试failover的slave收集FAILOVER_AUTH_ACK
5.超过半数后变成新Master
6.广播Pong通知其他集群节点。
A slave starts an election when the following conditions are met:
1 The slave's master is in FAIL state.
2 The master was serving a non-zero number of slots.
3 The slave replication link was disconnected from the master for no longer than a given amount of time, in order to ensure the promoted slave's data is reasonably fresh.
This time is user configurable.
|
3 主节点投票条件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
|
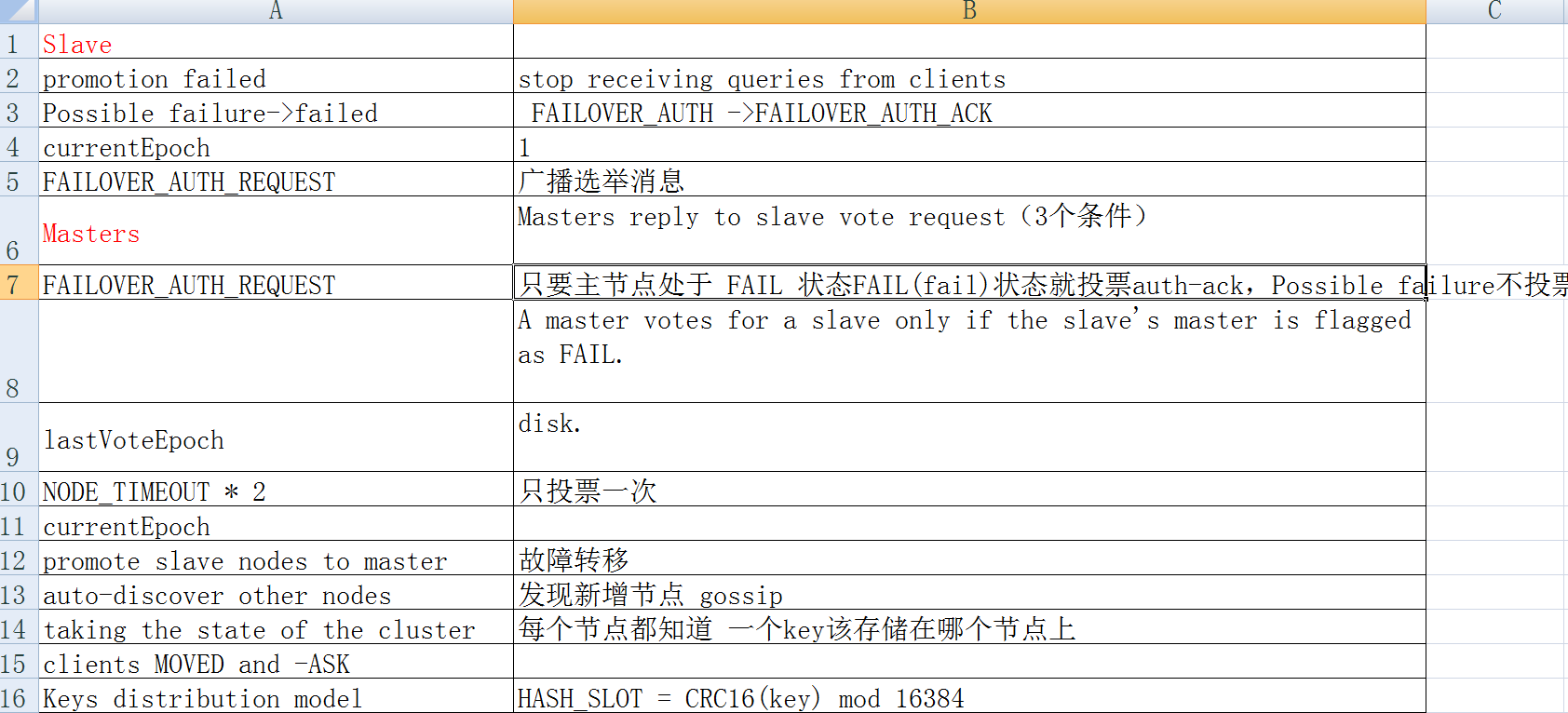
主节点接收到来自于从节点、要求以 FAILOVER_AUTH_REQUEST 请求的形式投票的请求。
要授予一个投票,必须要满足以下条件:
1) 在一个给定的时段(epoch)里,一个主节点只能投一次票,并且拒绝给以前时段投票:每个主节点都有一个 lastVoteEpoch 域,一旦认证请求数据包(auth request packet)里的 currentEpoch 小于 lastVoteEpoch,那么主节点就会拒绝再次投票。
当一个主节点积极响应一个投票请求,那么 lastVoteEpoch 会相应地进行更新。
2) 一个主节点投票给某个从节点当且仅当该从节点的主节点被标记为 FAIL。
3) 如果认证请求里的 currentEpoch 小于主节点里的 currentEpoch 的话,那么该请求会被忽视掉。
因此,主节点的回应总是带着和认证请求一致的 currentEpoch。
如果同一个从节点在增加 currentEpoch 后再次请求投票,那么保证一个来自于主节点的、旧的延迟回复不会被新一轮选举接受。
For a vote to be granted the following conditions need to be met:
1. A master only votes a single time for a given epoch, and refuses to vote for older epochs: every master has a lastVoteEpoch field and will refuse to vote again as long as the currentEpoch in the auth request packet is not greater than the lastVoteEpoch.
When a master replies positively to a vote request, the lastVoteEpoch is updated accordingly, and safely stored on disk.
2. A master votes for a slave only if the slave's master is flagged as FAIL.
3. Auth requests with a currentEpoch that is less than the master currentEpoch are ignored. Because of this the master reply will always have the same currentEpoch as the auth request. If the same slave asks again to be voted, incrementing the currentEpoch, it is guaranteed that an old delayed reply from the master can not be accepted for the new vote.
/* Vote for the node asking for our vote if there are the conditions. */
// 在条件满足的情况下,为请求进行故障转移的节点 node 进行投票,支持它进行故障转移
///主节点投票
void clusterSendFailoverAuthIfNeeded(clusterNode *node, clusterMsg *request) {
// 请求节点的主节点
clusterNode *master = node->slaveof;
// 请求节点的当前配置纪元
uint64_t requestCurrentEpoch = ntohu64(request->currentEpoch);
// 请求节点想要获得投票的纪元
uint64_t requestConfigEpoch = ntohu64(request->configEpoch);
// 请求节点的槽布局
unsigned char *claimed_slots = request->myslots;
int force_ack = request->mflags[0] & CLUSTERMSG_FLAG0_FORCEACK;
int j;
/* IF we are not a master serving at least 1 slot, we don't have the
* right to vote, as the cluster size in Redis Cluster is the number
* of masters serving at least one slot, and quorum is the cluster
* size + 1 */
// 如果节点为从节点,或者是一个没有处理任何槽的主节点,
// 那么它没有投票权
if (nodeIsSlave(myself) || myself->numslots == 0) return;
/* Request epoch must be >= our currentEpoch. */
// 请求的配置纪元必须大于等于当前节点的配置纪元
if (requestCurrentEpoch < server.cluster->currentEpoch) return;
/* I already voted for this epoch? Return ASAP. */
// 已经投过票了
if (server.cluster->lastVoteEpoch == server.cluster->currentEpoch) return;
/* Node must be a slave and its master down.
* The master can be non failing if the request is flagged
* with CLUSTERMSG_FLAG0_FORCEACK (manual failover). */
if (nodeIsMaster(node) || master == NULL ||
(!nodeFailed(master) && !force_ack)) return;
/* We did not voted for a slave about this master for two
* times the node timeout. This is not strictly needed for correctness
* of the algorithm but makes the base case more linear. */
// 如果之前一段时间已经对请求节点进行过投票,那么不进行投票
if (mstime() - node->slaveof->voted_time < server.cluster_node_timeout * 2)
return;
/* The slave requesting the vote must have a configEpoch for the claimed
* slots that is >= the one of the masters currently serving the same
* slots in the current configuration. */
for (j = 0; j < REDIS_CLUSTER_SLOTS; j++) {
// 跳过未指派节点
if (bitmapTestBit(claimed_slots, j) == 0) continue;
// 查找是否有某个槽的配置纪元大于节点请求的纪元
if (server.cluster->slots[j] == NULL ||
server.cluster->slots[j]->configEpoch <= requestConfigEpoch)
{
continue;
}
// 如果有的话,说明节点请求的纪元已经过期,没有必要进行投票
/* If we reached this point we found a slot that in our current slots
* is served by a master with a greater configEpoch than the one claimed
* by the slave requesting our vote. Refuse to vote for this slave. */
return;
}
/* We can vote for this slave. */
// 为节点投票
clusterSendFailoverAuth(node);
// 更新时间值
server.cluster->lastVoteEpoch = server.cluster->currentEpoch;
node->slaveof->voted_time = mstime();
}
|
4. Redis Cluster数据分片机制
A 问题(读三遍):Redis的数据如何平滑扩容?
关键词:扩容,还有平滑
为了使得集群能够水平扩展,首要解决的问题就是如何将整个数据集按照一定的规则分配到多个节点上,
平滑扩容是一种在线水平扩容方式,既把原有的分库平滑迁移到新添加的 RDS 实例上
扩展 :nginx,Strom等其他任何一个服务上
B 思考:
常用的数据分片的方法有:范围分片,哈希分片,一致性哈希算法和虚拟哈希槽等
范围分片:一旦固定,范围就无法改变
哈希分片,如果想增加一个节点,整个集群的数据完全打破,这就是问题
Redis Cluster 采用虚拟哈希槽分区,所有的键根据哈希函数映射到 0 ~ 16383 整数槽内,计算公式:slot = CRC16(key) & 16383。
每一个节点负责维护一部分槽以及槽所映射的键值数据
c 回答
-
一个大数据拆分不同小数据,slot,分批迁移。
-
集群状态,清楚知道每个sloat位置
#2 陈咬金第二斧 clusterCron 过程
每间隔 100 毫秒执行一次
-
向集群中的所有断线或者未连接节点发送CLUSTERMSG_TYPE_PING 消息
-
隔一秒钟,随机5个节点发送CLUSTERMSG_TYPE_PING 信息
-
遍历所有节点,检查是否需要将某个节点标记为下线
3.1.如果tcp链接断开,释放链接,下次会在1步骤中重新建立链接
3.2 如果该链接没有发送过ping,没有随机到,发送ping 信息
3.3 计算当前时间和该节点上次发送ping时间,如果超过cluster_node_timeout
标记 REDIS_NODE_PFAIL 疑似下线标记
3.3 如果从节点没有在复制主节点,那么对从节点进行设置【why】
3.4 从节点发起故障转移 clusterHandleSlaveFailover
clusterHandleManualFailover –表示没看懂
clusterHandleSlaveMigration –表示没看懂
3.5 更新集群的节点状态信息 !!!! —REDIS_NODE_PFAIL REDIS_CLUSTER_FAIL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
/* Compute the cluster size, that is the number of master nodes
* serving at least a single slot.
*
* At the same time count the number of unreachable masters with
* at least one node. */
// 统计在线并且正在处理至少一个槽的 master 的数量,
// 以及下线 master 的数量
{
dictIterator *di;
dictEntry *de;
server.cluster->size = 0;
di = dictGetSafeIterator(server.cluster->nodes);
while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL) {
clusterNode *node = dictGetVal(de);
if (nodeIsMaster(node) && node->numslots) {
server.cluster->size++;
if (node->flags & (REDIS_NODE_FAIL|REDIS_NODE_PFAIL))
unreachable_masters++;
}
}
dictReleaseIterator(di);
}
/* If we can't reach at least half the masters, change the cluster state
* to FAIL, as we are not even able to mark nodes as FAIL in this side
* of the netsplit because of lack of majority.
*
* 如果不能连接到半数以上节点,那么将我们自己的状态设置为 FAIL
* 因为在少于半数节点的情况下,节点是无法将一个节点判断为 FAIL 的。
*/
{
int needed_quorum = (server.cluster->size / 2) + 1;
if (unreachable_masters >= needed_quorum) {
new_state = REDIS_CLUSTER_FAIL;
among_minority_time = mstime();
}
}
|
clusterHandleSlaveFailover 故障转移流程
将当前节点的身份由从节点改为主节点
让从节点取消复制,成为新的主节点
接收所有主节点负责处理的槽
更新集群配置纪元
更新节点状态
并保存配置文件
第二天:what is clusterCron
A 学习资料:
clusterCron
B 学习输出:有限状态机
有限状态机是个十分有用的模型,可以用来模拟世界上大部分的事物,其有三个特征:
- 状态总数(state)是有限的。
- 任一时刻,只处在一种状态之中。
- 某种条件下,会从一种状态转变(transition)到另一种状态。

JavaScript与有限状态机
一个有特色的有限状态机
TCP Operational Overview and the TCP Finite State Machine (FSM)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qa6csfkK7_I
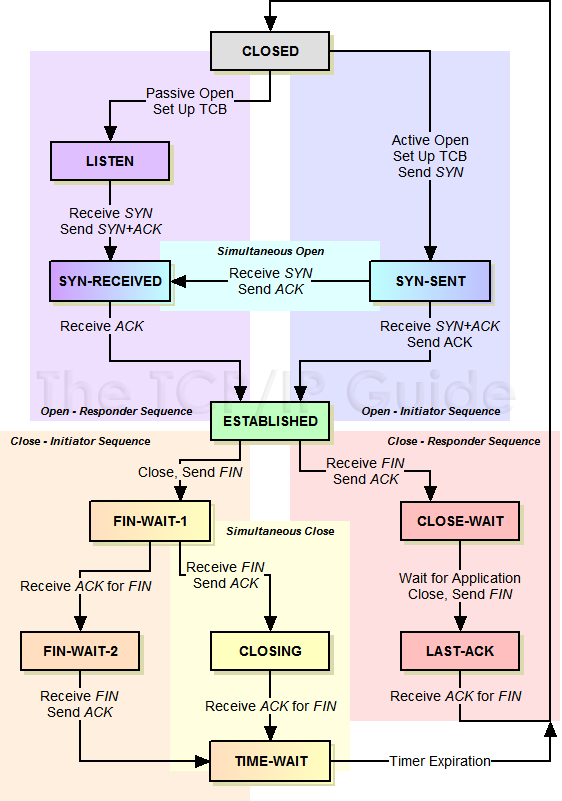
#陈咬金第一斧 模型什么
#陈咬金第二斧 状态状态是什么
#陈咬金第三斧 有什么用
第三天: 内存模型(对象的类型与编码)
zset
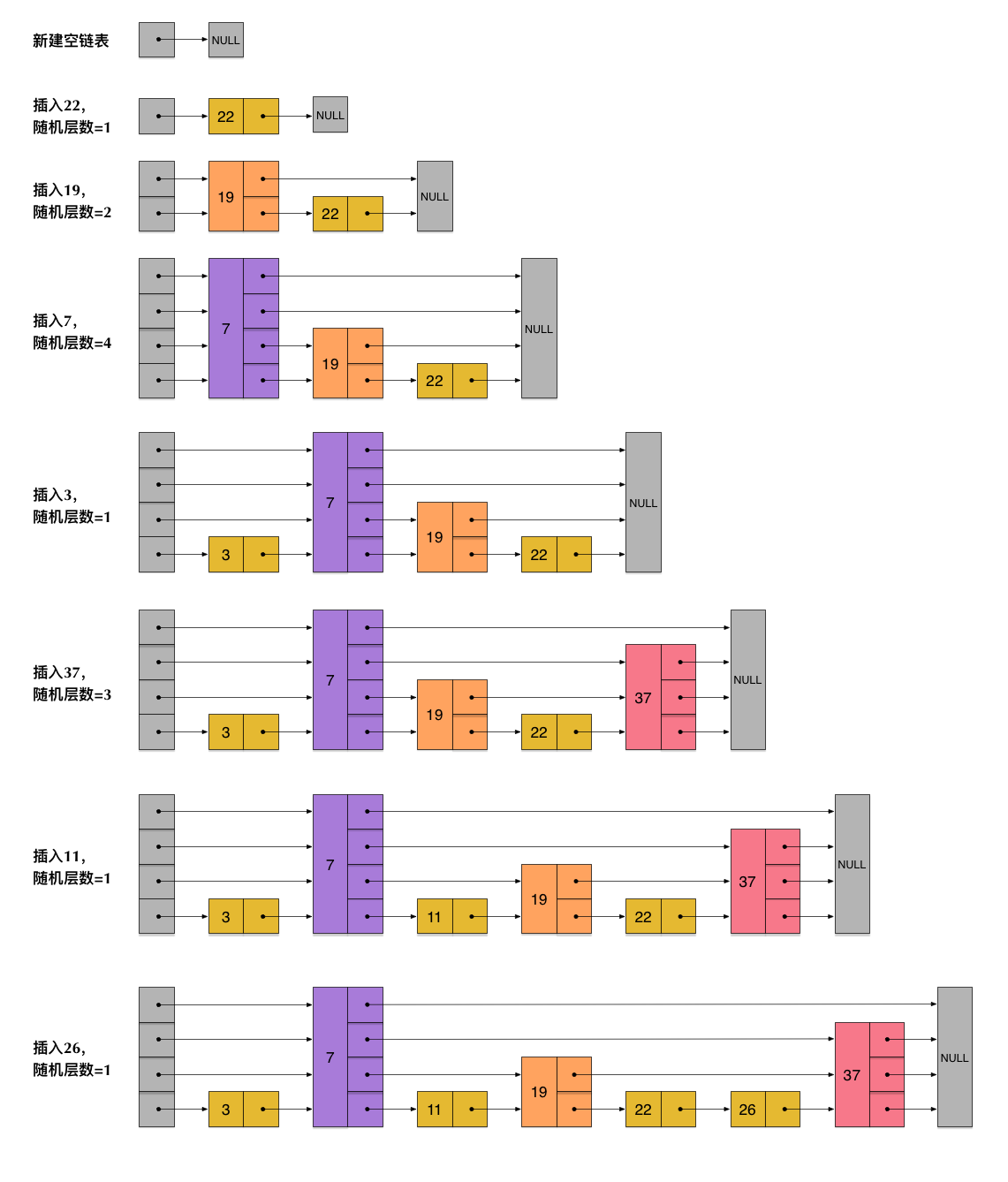
#1【插入操作】
zskiplistNode *zslInsert(zskiplist *zsl, double score, robj *obj)
文字描述:
- 在各个层查找节点的插入位置 存储 zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL]
- level = zslRandomLevel()
- 插入节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
|
/*
* 创建一个成员为 obj ,分值为 score 的新节点,
* 并将这个新节点插入到跳跃表 zsl 中。
*
* 函数的返回值为新节点。
*
* T_wrost = O(N^2), T_avg = O(N log N)
*/
zskiplistNode *zslInsert(zskiplist *zsl, double score, robj *obj) {
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;
unsigned int rank[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL];
int i, level;
redisAssert(!isnan(score));
// 在各个层查找节点的插入位置
// T_wrost = O(N^2), T_avg = O(N log N)
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
/* store rank that is crossed to reach the insert position */
// 如果 i 不是 zsl->level-1 层
// 那么 i 层的起始 rank 值为 i+1 层的 rank 值
// 各个层的 rank 值一层层累积
// 最终 rank[0] 的值加一就是新节点的前置节点的排位
// rank[0] 会在后面成为计算 span 值和 rank 值的基础
rank[i] = i == (zsl->level-1) ? 0 : rank[i+1];
// 沿着前进指针遍历跳跃表
// T_wrost = O(N^2), T_avg = O(N log N)
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
// 比对分值
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
// 比对成员, T = O(N)
compareStringObjects(x->level[i].forward->obj,obj) < 0))) {
// 记录沿途跨越了多少个节点
rank[i] += x->level[i].span;
// 移动至下一指针
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
// 记录将要和新节点相连接的节点
update[i] = x;
}
/* we assume the key is not already inside, since we allow duplicated
* scores, and the re-insertion of score and redis object should never
* happen since the caller of zslInsert() should test in the hash table
* if the element is already inside or not.
*
* zslInsert() 的调用者会确保同分值且同成员的元素不会出现,
* 所以这里不需要进一步进行检查,可以直接创建新元素。
*/
// 获取一个随机值作为新节点的层数
// T = O(N)
level = zslRandomLevel();
// 如果新节点的层数比表中其他节点的层数都要大
// 那么初始化表头节点中未使用的层,并将它们记录到 update 数组中
// 将来也指向新节点
if (level > zsl->level) {
// 初始化未使用层
// T = O(1)
for (i = zsl->level; i < level; i++) {
rank[i] = 0;
update[i] = zsl->header;
update[i]->level[i].span = zsl->length;
}
// 更新表中节点最大层数
zsl->level = level;
}
// 创建新节点
x = zslCreateNode(level,score,obj);
// 将前面记录的指针指向新节点,并做相应的设置
// T = O(1)
for (i = 0; i < level; i++) {
// 设置新节点的 forward 指针
x->level[i].forward = update[i]->level[i].forward;
// 将沿途记录的各个节点的 forward 指针指向新节点
update[i]->level[i].forward = x;
/* update span covered by update[i] as x is inserted here */
// 计算新节点跨越的节点数量
x->level[i].span = update[i]->level[i].span - (rank[0] - rank[i]);
// 更新新节点插入之后,沿途节点的 span 值
// 其中的 +1 计算的是新节点
update[i]->level[i].span = (rank[0] - rank[i]) + 1;
}
/* increment span for untouched levels */
// 未接触的节点的 span 值也需要增一,这些节点直接从表头指向新节点
// T = O(1)
for (i = level; i < zsl->level; i++) {
update[i]->level[i].span++;
}
// 设置新节点的后退指针
x->backward = (update[0] == zsl->header) ? NULL : update[0];
if (x->level[0].forward)
x->level[0].forward->backward = x;
else
zsl->tail = x;
// 跳跃表的节点计数增一
zsl->length++;
return x;
}
|
3.2
- hash使用读大于写场景:频繁等值查找,少量更新。(why 不完美地方分析)
- hash是无序存储的,如果实现order by ,group by ,范围查找 hash需要消耗额外空间和时间。
- hash 连续空间(不冲突),更新:删除操作 桶上元素后,空间大小不会变少,链表,tree灵活,插入:扩容
- 字符串作为hash key 性能不如int

1
2
3
|
127.0.0.1:6379> debug object page_rank
Value at:0x7f01844863e0 refcount:1 encoding:skiplist serializedlength:53 lru:16526412 lru_seconds_idle:789
|
第四天: 发布-订阅(Publish-Subscribe)
参考资料

https://juejin.im/post/59fef3846fb9a0450f215096
输出
第五天 一个完整Socket过程
5.1 参考资料
Redis client/server 交互步骤分为以下 6 个步骤:
一、Client 发起 socket 连接
二、Server 接受 socket 连接
三、客户端 开始写入
四、server 端接收写入
五、server 返回写入结果
六、Client 收到返回结
5.2 理解输出
#陈咬金第一斧 模型什么
#陈咬金第二斧 状态状态是什么
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
typedef struct aeEventLoop {
// 已注册的文件事件
aeFileEvent *events; /* Registered events */
// 已就绪的文件事件
aeFiredEvent *fired; /* Fired events */ 着2个有什么关系?
// 时间事件
aeTimeEvent *timeEventHead;
} aeEventLoop;
readQueryFromClient
sendReplyToClient
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/28098563/errno-after-accept-in-linux-socket-programming
|
#陈咬金第三斧 有什么用
第三天 crash 如何查看指标
#陈咬金第一斧 解决crash思路是什么
#陈咬金第二斧 步骤是什么
#陈咬金第三斧 有什么用
#陈咬金第二斧 执行步骤是什么 info
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
|
https://www.cnblogs.com/nulige/p/10708900.html
Redis-5.0.5
wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-5.0.5.tar.gz
启动:
systemctl start redis.service
配置:/etc/redis.conf
redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> info
# Server
redis_version:3.2.3
redis_git_sha1:00000000
redis_git_dirty:0
redis_build_id:672aed6eb816ad6c
redis_mode:standalone
os:Linux 3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64 x86_64
arch_bits:64
multiplexing_api:epoll Redis 所使用的事件处理机制
gcc_version:4.8.5 Redis 所使用的事件处理机制
process_id:24414 服务器进程的 PID
run_id:f7397d0e9c3d60ac64376365c905ff14f14b3118 Redis 服务器的随机标识符(用于 Sentinel 和集群)
tcp_port:6379
uptime_in_seconds:145
uptime_in_days:0
hz:10
lru_clock:1579188
executable:/usr/bin/redis-server
config_file:/etc/redis.conf
# Clients
connected_clients:1
client_longest_output_list:0
client_biggest_input_buf:0
blocked_clients:0
# Memory
used_memory:813096 由 Redis 分配器分配的内存总量,以字节(byte)为单位
used_memory_human:794.04K 以人类可读的格式返回 Redis 分配的内存总量
used_memory_rss:5943296
从操作系统的角度,返回 Redis 已分配的内存总量(俗称常驻集大小)。这个值和top 、 ps 等命令的输出一致。
mem_allocator:jemalloc-3.6.0
# Persistence
loading:0
rdb_changes_since_last_save:0
rdb_bgsave_in_progress:0
rdb_last_save_time:1578637347
rdb_last_bgsave_status:ok
rdb_last_bgsave_time_sec:-1
rdb_current_bgsave_time_sec:-1
aof_enabled:0
aof_rewrite_in_progress:0
aof_rewrite_scheduled:0
aof_last_rewrite_time_sec:-1
aof_current_rewrite_time_sec:-1
aof_last_bgrewrite_status:ok
aof_last_write_status:ok
# Stats
total_connections_received:1
total_commands_processed:3
instantaneous_ops_per_sec:0
total_net_input_bytes:134
total_net_output_bytes:5929399
instantaneous_input_kbps:0.00
instantaneous_output_kbps:0.00
rejected_connections:0
sync_full:0
sync_partial_ok:0
sync_partial_err:0
expired_keys:0
evicted_keys:0
keyspace_hits:0
keyspace_misses:0
pubsub_channels:0
pubsub_patterns:0
latest_fork_usec:0
migrate_cached_sockets:0
# Replication
role:master
connected_slaves:0
master_repl_offset:0
repl_backlog_active:0
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:0
repl_backlog_histlen:0
# CPU
used_cpu_sys:0.11
used_cpu_user:0.04
used_cpu_sys_children:0.00
used_cpu_user_children:0.00
# Cluster
cluster_enabled:0
|
-
延迟时间
1
|
Redis-cli --latency -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379
|
-
used_memory_rss含义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
https://redis.io/commands/info
When rss >> used, a large difference means there is memory fragmentation (internal or external), 说明碎片率严重
When used >> rss, it means part of Redis memory has been swapped off by the operating system:
Redis进程内消耗主要包括:自身内存(少,3M 忽视掉)+对象内存(数据多,没办法)+缓冲内存(客户端缓冲、复制积压缓冲区、AOF缓冲区。)+内存碎片(比如当保存5KB对象时jemalloc可能会采用8KB的块存储,而剩下的3KB空间变为了内存碎片不能再分配给其他对象存储)
频繁做更新操作
大量过期键删除
|
题外话:
ptmalloc的缺陷: 不定期分配长生命周期的内存容易造成内存碎片,不利于回收。 多线程锁开销大, 需要避免多线程频繁分配释放。 * 内存从thread的areana中分配, 内存不能从一个arena移动到另一个arena, 就是说如果多线程使用内存不均衡,容易导致内存的浪费
tcmalloc内存碎片
不理解
malloc_trim
第四天 redis.60 多线程
二、redis设计与实现
2.1 看图说话:二叉树,M叉树,跳表查找一个记录,前进的概率是多少?
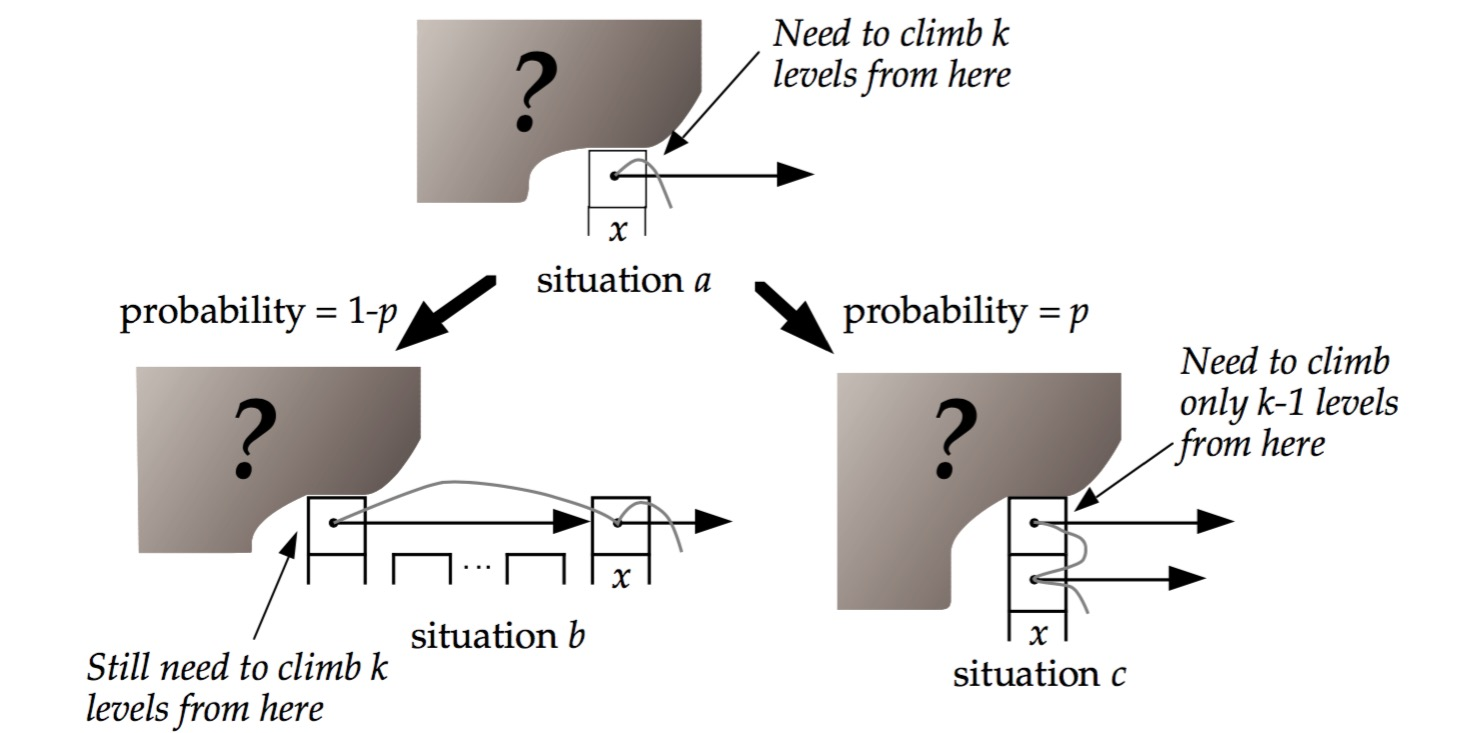
- 看图回答